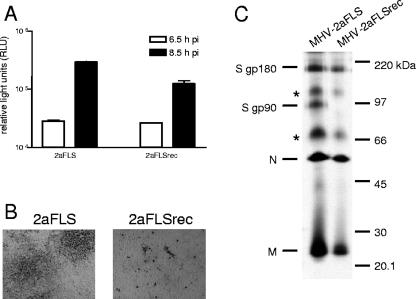
FIG. 2.
Infection of murine cells. (A) LR7 cells were inoculated with MHV-2aFLS or MHV-2aFLSrec at a multiplicity of infection of 1. At the indicated time points postinfection (pi), the cells were lysed and intracellular luciferase expression was determined by using a luminometer (values are expressed in relative light units, RLU). Standard deviations are indicated. (B) Plaque phenotypes of recombinant viruses on LR7 cells. At 18 h postinfection, cells were fixed with a 3% formaldehyde solution, after which the agar overlay was removed. After being permeabilized with 1% Triton X-100 in phosphate-buffered saline, viral antigen was detected with the anti-MHV serum k134 at a 1:400 dilution. Peroxidase-conjugated swine immunoglobulins to rabbit immunoglobulins (Dakopatts) were used as secondary antibodies at a 1:100 dilution. Peroxidase was visualized, using an AEC substrate kit from Vector laboratories. Pictures were taken using bright-field microscopy and a Nikon DS-L1 digital camera. (C) LR7 cells were infected with the recombinant viruses indicated on the top of the gel at a multiplicity of infection of 10. Cells were labeled for 3 h with 35S-labeled amino acids (Amersham), starting 5 h postinfection. At the end of the labeling period, culture media were collected and prepared for immunoprecipitation with the anti-MHV serum k134, followed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, followed by fluorography, as previously described (10). The positions of the different viral proteins are indicated on the left, while the molecular mass marker is indicated on the right. Asterisks indicate higher-order structures of the M and/or N proteins.