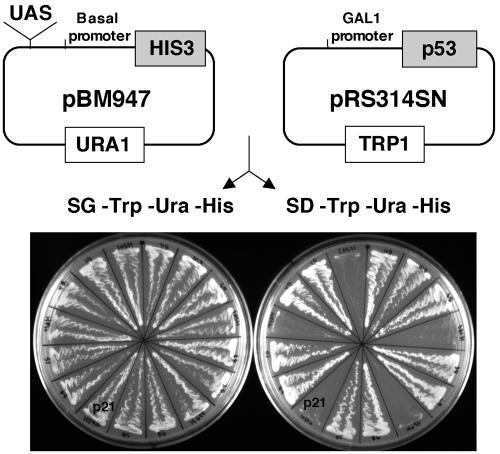
FIG. 2.
Yeast selection system. The candidate upstream activating sequences (UAS) recovered from ChIP were cloned into the pBM947 reporter vector containing the HIS3 gene under the control of a basal GAL1 promoter and a URA1 marker. The pBM947-based library was transformed into an auxotrophic His-deficient yeast strain containing the pRS314SN vector, which expresses a galactose-inducible human wild-type p53 and a TRP1 marker. Yeasts containing both the vectors were grown on galactose-containing, histidine-deficient media (SG-Trp-Ura-His) to assay for the ability of p53 to bind to the potential UAS in the pBM947 vector and activate transcription of the HIS3 gene. Replica plating of all clones on glucose-containing, histidine-deficient media (SD-Trp-Ura-His) was performed to rule out false-positive clones. The clones that grew in the presence of glucose were considered false positive, and only the clones that grew on galactose, and presumably in a p53-dependent manner, were analyzed further. A clone containing a fragment of the p21 promoter encompassing site 1 is indicated as an example of a positive result.