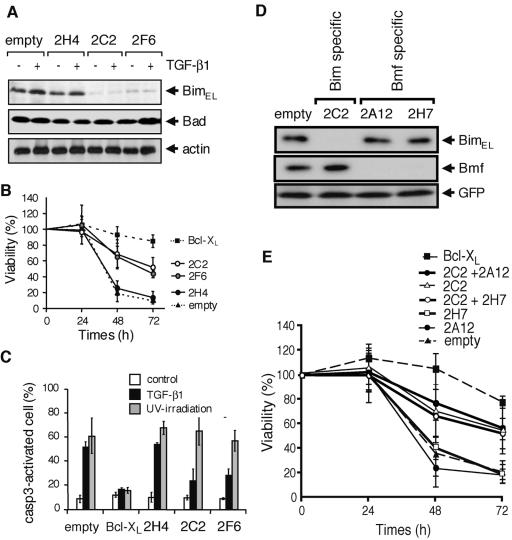
FIG. 6.
Reduction of Bim expression by the RNAi method renders SNU16 cells resistant to TGF-β1-induced apoptosis, but that of Bmf-expression does not. (A) SNU16 cells were transfected with an expression vector encoding Bim-specific shRNA (2H4, 2C2, or 2F6) together with the puromycin-resistant gene and then cultured with 1 μg/ml puromycin for 3 days. Viable cells were incubated with 10 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 24 h and then subjected to Western blotting with antibodies to Bim, Bad, or actin. (B) SNU16 cells were transfected with an expression vector for the indicated shRNA or with a Bcl-XL expression vector together with GFP and then incubated with 10 ng/ml TGF-β1 for the period indicated. Transfected cells were lysed, and the fluorescence intensity of GFP was quantified. Cell viability was determined from the ratio of fluorescence before and after the treatment with TGF-β1. Means ± SD of three independent experiments are shown. (C) Activation of caspase-3 (casp3) was analyzed as described for Fig. 2D and Fig. 3 for TGF-β1-treated or UV-irradiated SNU16 cells transfected with expression vectors for the indicated shRNA or Bcl-XL as in described for panel B. Experiments were performed three times, and the means ± SD for caspase-3-activated cells in the GFP-positive population are indicated. (D) SNU16 cells were transfected with an empty vector or vectors for Bim-specific shRNA (2C2) or Bmf-specific shRNA (2A12 and 2H7) together with FLAG-tagged BimEL or Bmf expression vectors. Total cell lysate was extracted and subjected to Western blotting using anti-FLAG M2 antibody. (E) SNU16 cells were transfected with expression vectors for Bcl-XL, Bim-specific shRNA (2C2), and/or Bmf-specific shRNA (2A12 and 2H7) together with that of GFP, and then cell viability was quantified after the treatment with TGF-β1 as described for panel B. Means ± SD of three independent experiments are shown.