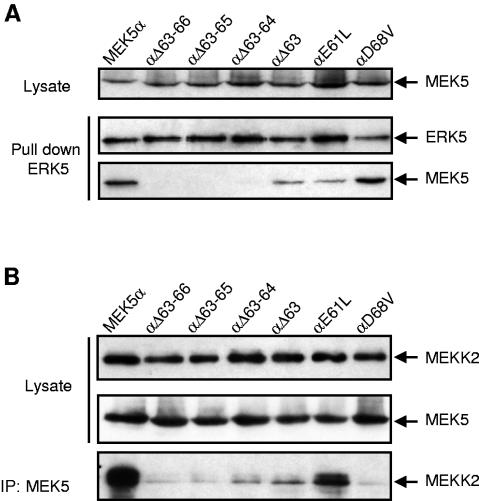
FIG. 5.
Characterization of the ERK5 docking site in the N terminus of MEK5α. (A) Bacterially expressed His-ERK5 (1 μg) was incubated with extracts of COS-7 cells transfected with the expression vectors encoding wild-type or mutant MEK5α fused to GST. ERK5 was isolated by incubation with Ni2+-NTA beads. The binding of MEK5 was examined by immunoblot analysis with an antibody to the GST epitope tag. (B) COS-7 cells were cotransfected with expression vectors encoding wild-type or mutant GST-MEK5α with HA-tagged MEKK2. MEK5 was isolated following precipitation with an anti-GST antibody. The binding of MEKK2 was examined by immunoblot analysis with an antibody to the HA epitope tag. The expression of MEK5 (A and B) and MEKK2 (B) in cell lysates and the presence of ERK5 (A) in the immune complexes were detected by immunoblot analysis using an anti-GST, an anti-HA, and an anti-ERK5 antibody, respectively.