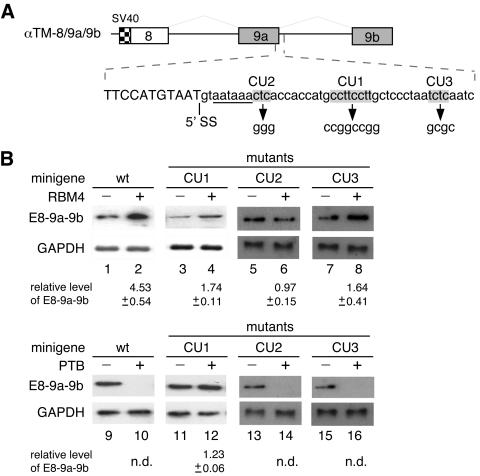
FIG. 5.
RBM4 and PTB exert opposite effects on utilization of α-TM exon 9a via an intronic CU-rich element. (A) The diagram shows the sequence around the splice junction (5′ SS) of α-TM exon 9a. The mutant reporters contain pyrimidine-to-guanine changes in each CU-rich element (shown in gray). The polyadenylation signal is underlined. (B) The wild-type and mutant pTM-8/9a/9b minigenes were each cotransfected into HEK 293 cells along with an empty vector or with expression vector encoding FLAG-RBM4 (lanes 1 through 8) or FLAG-PTB (lanes 9 through 16). As in Fig. 4, the splicing products were examined by RT-PCR followed by blotting analysis. GAPDH was used as a normalization control. Relative levels of E8-9a-9b RNA are indicated below the gels. n.d., not detectable.