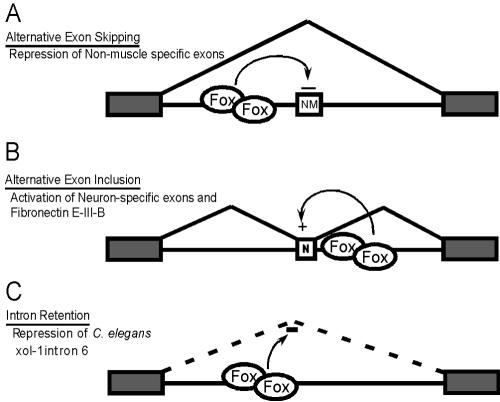
FIG. 8.
Fox proteins bind to introns to influence the splicing of adjacent exons by multiple mechanisms. (A) Fox promotes exon skipping. In muscle cells, Fox proteins bind upstream of a non-muscle-specific exon (NM) to promote skipping (22). (B) Fox promotes exon inclusion. As described here, Fox proteins bind downstream of a neuron-specific exon (N) or the fibronectin EIIIB exon and activate splicing. (C) Fox promotes intron retention. Intron 6 of the C. elegans Xol-1 transcript is spliced poorly in the presence of C. elegans Fox-1 (43). The protein may bind to this intron to decrease its splicing efficiency.