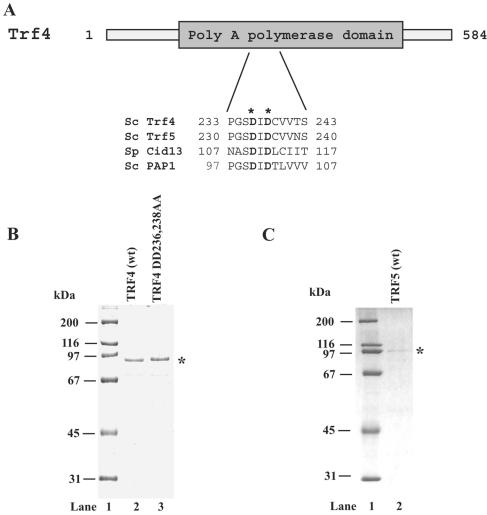
FIG. 1.
Purity of wild-type Trf4 and Trf5 proteins and of active-site mutant Trf4 protein. (A) Schematic representation of Trf4. The conserved sequence motif characteristic for the Pol β family is shown as a gray box. A highly conserved region known to be involved in metal binding and catalysis was aligned for the S. cerevisiae (Sc) Trf4 and Trf5, S. pombe (Sp) Cid13, and the S. cerevisiae canonical PAP enzyme. The conserved catalytic aspartates at positions 236 and 238 in Trf4, which correspond to the metal-binding aspartates at positions 100 and 102 in the canonical PAP are indicated by asterisks. (B) Purified Trf4 and mutant Trf4 DD236,238AA, in which aspartates at positions 236 and 238 have been changed to alanines, were analyzed on a 10% denaturing polyacrylamide gel and stained with Coomassie blue. The position of the purified proteins is indicated by an asterisk. Lane 1, molecular mass standards; lane 2, 0.5 μg of wild-type (wt) Trf4 protein; lane 3, 0.5 μg of Trf4 DD236,238AA protein. (C) Purified Trf5 protein (150 ng). The position of purified Trf5 is indicated by an asterisk.