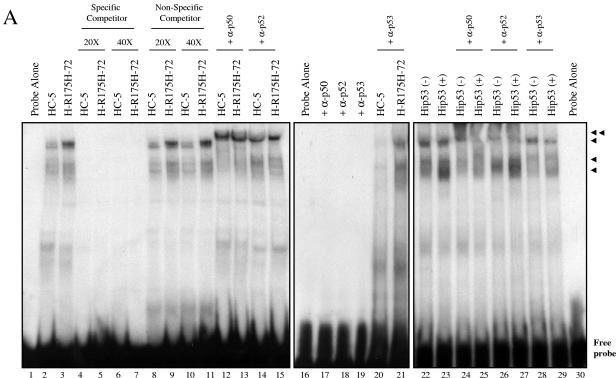
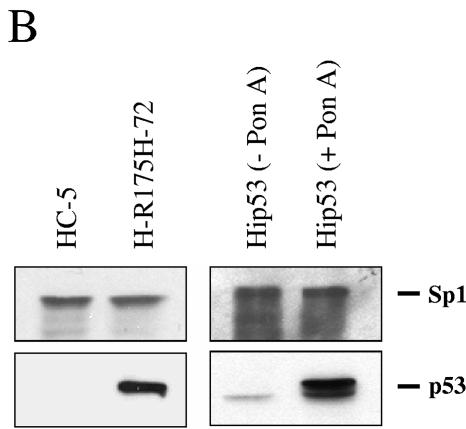
FIG. 7.
H1299 cells expressing mutant p53-R175H show increased binding to the NF-κB site. (A) Nuclear extracts of HC-5 and H-R175H were incubated as described in Materials and Methods with a 32P-labeled probe containing the sequence of the NF-κB DNA-binding site. Competition studies were done using a specific competitor (lanes 4 to 7) and a nonspecific competitor (lanes 8 to 11) at both 20× (lanes 4, 5, 8, and 9) and 40× (lanes 6, 7, 10, and 11) molar excess. The single arrows indicate the DNA complexes containing NF-κB complexes. Increased NF-κB activity is observed in the presence of mutant p53 (lanes 2, 3, and 8 to 11). The double arrow indicates the supershifted complex in the presence of antibodies specific for NF-κB1 (p50), NF-κB2 (p52), and p53 (lanes 12 to 15, 20 to 21, and 24 to 29, respectively). Equal amounts of protein were added to each lane. (B) In a parallel experiment, nuclear fractions prepared for the DNA-binding experiment were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Sp1 and p53 were detected by Western blotting to evaluate the equal loading of protein and the presence of p53 during the shift assay experiment.