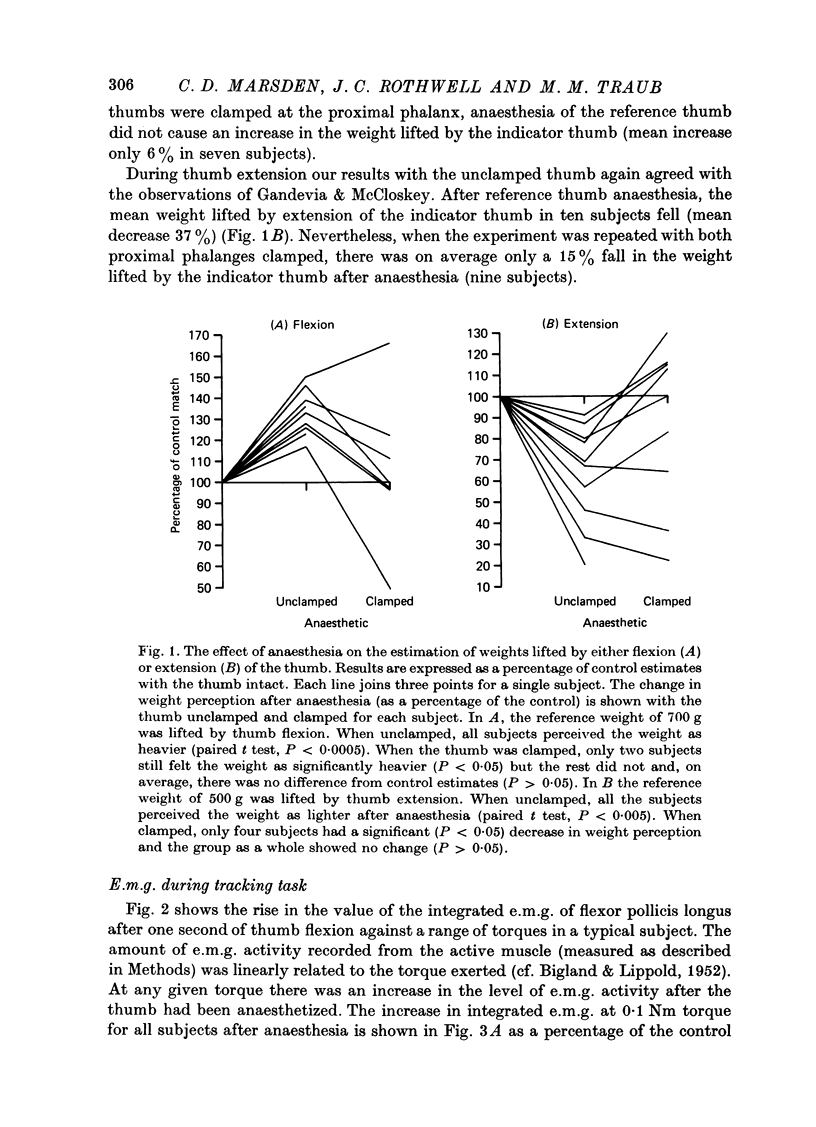
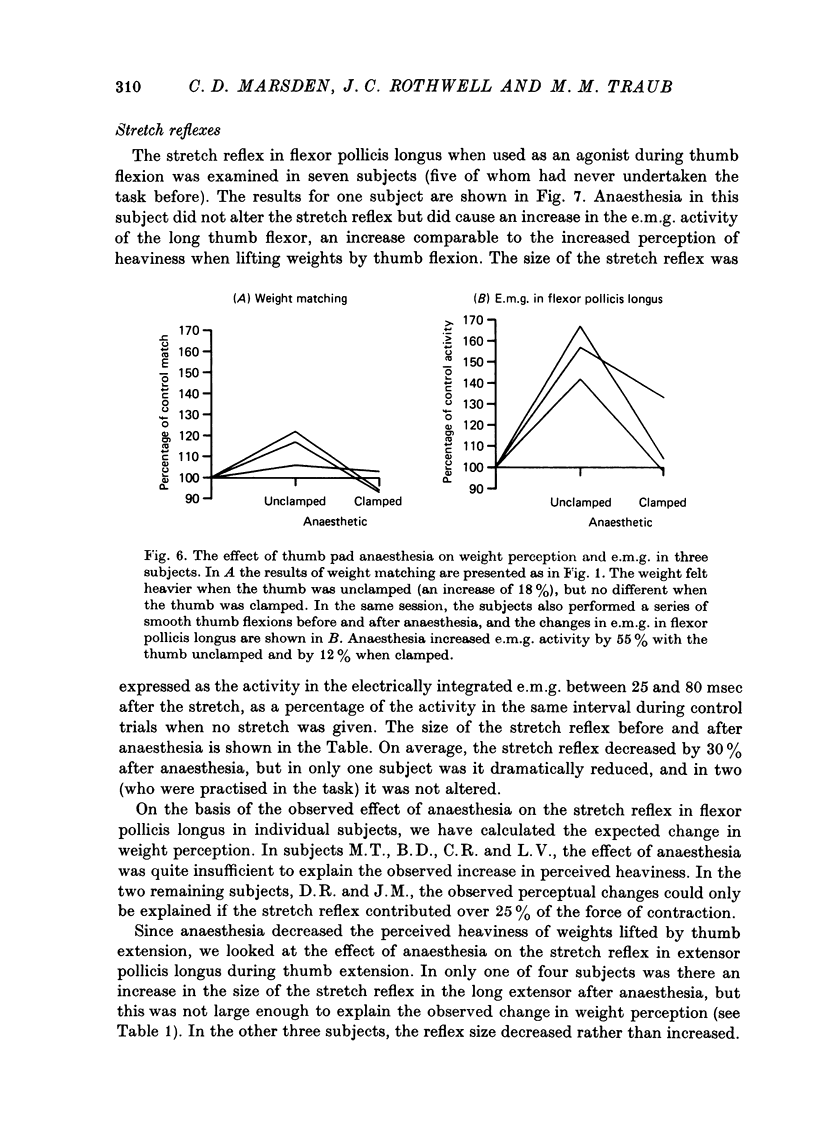
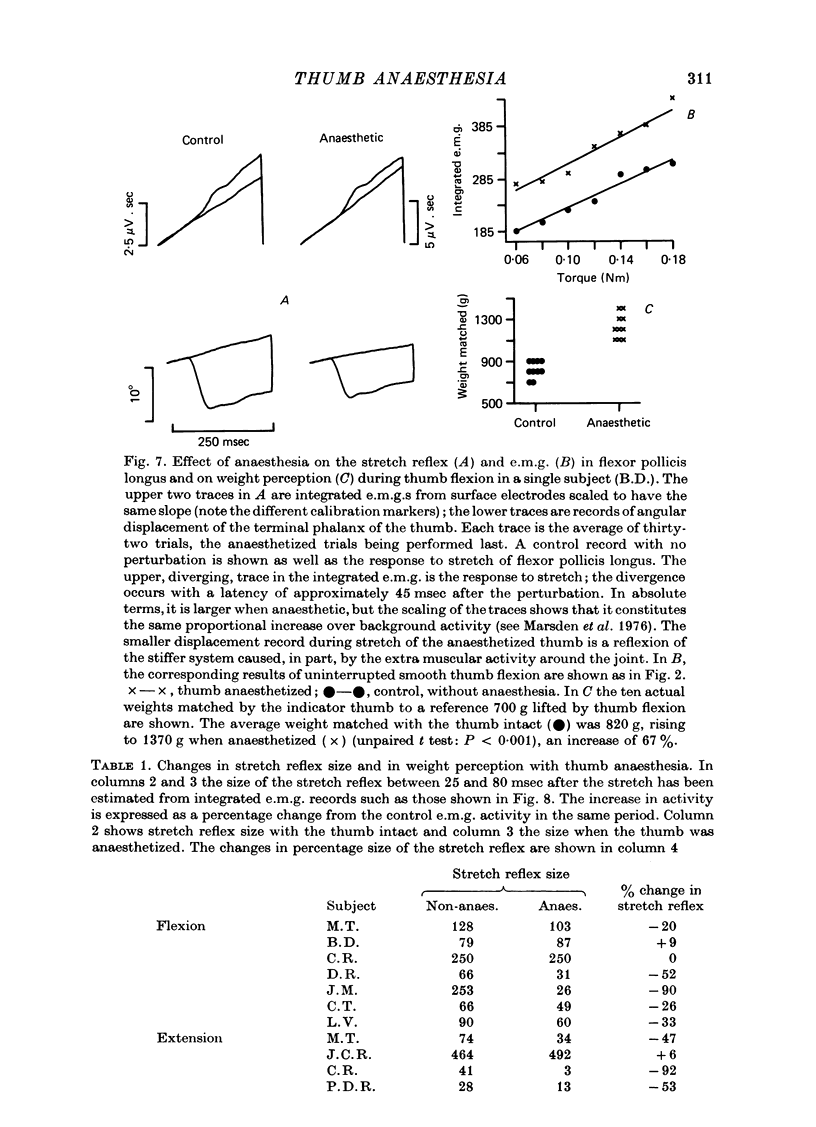
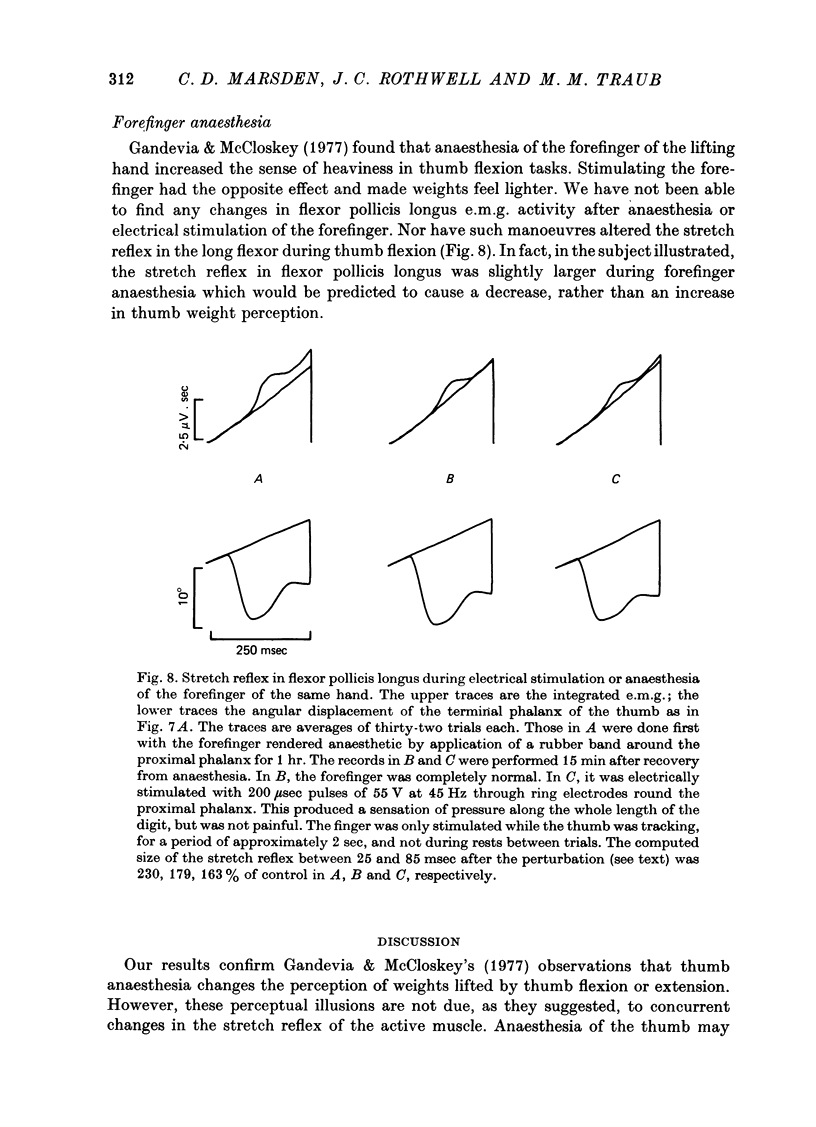
Abstract
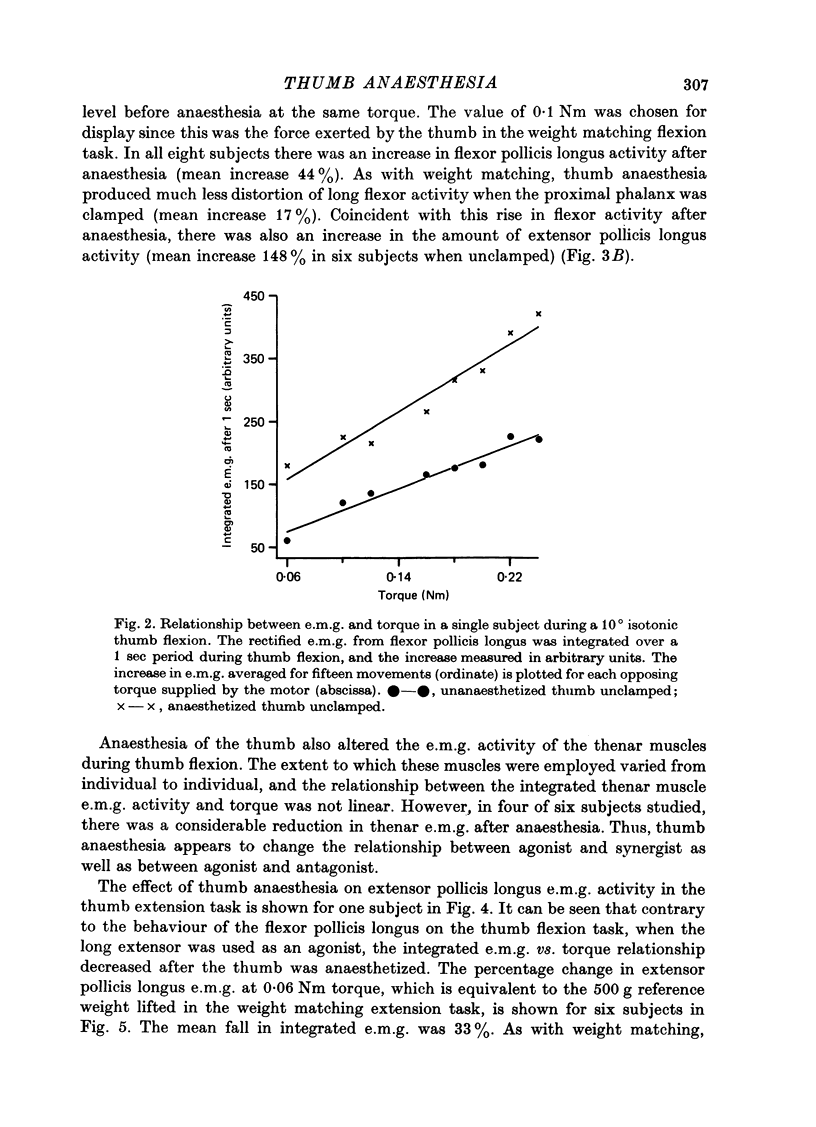
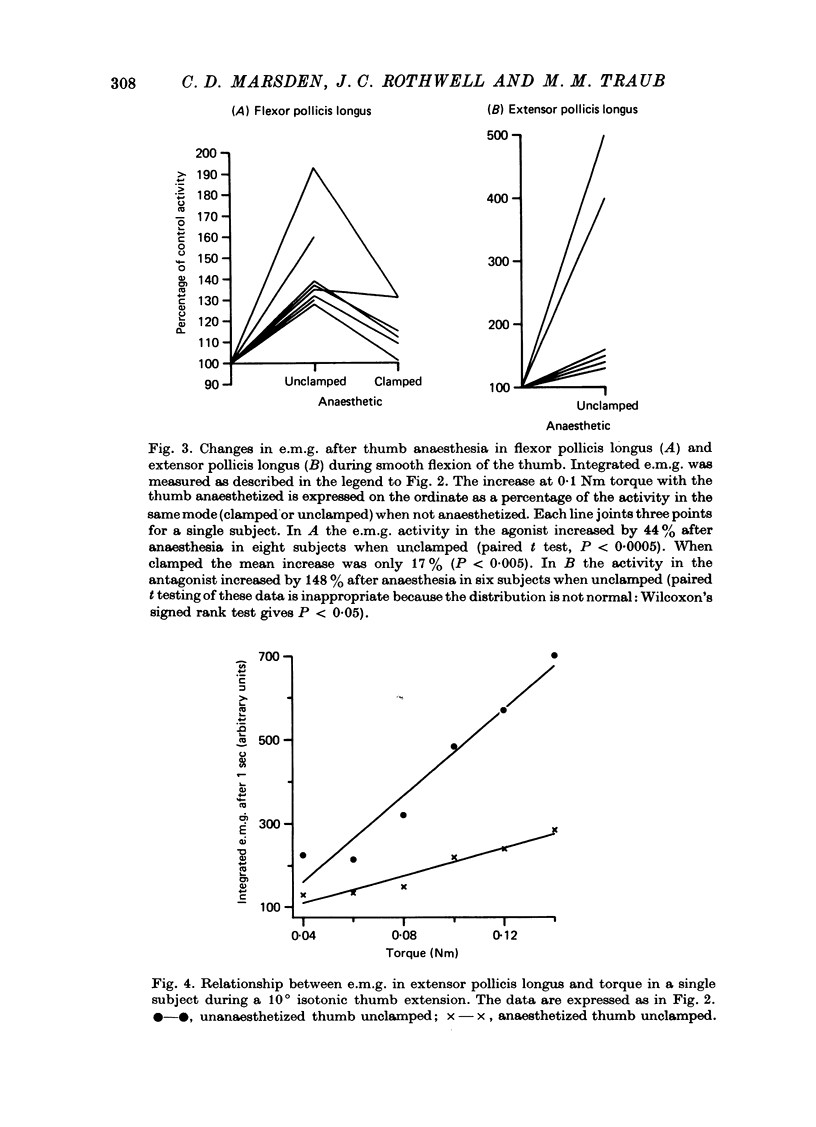
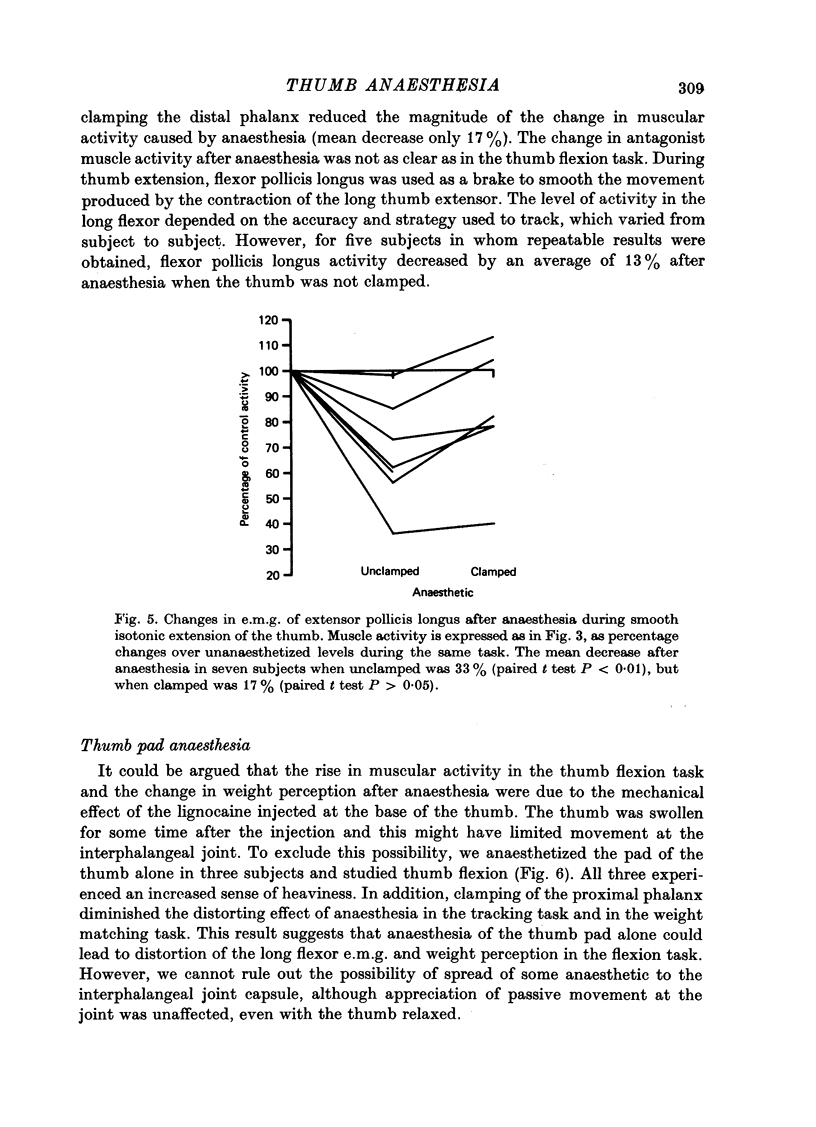
1. We have confirmed the results of Gandevia & McCloskey (1977) on the effect of thumb anaesthesia on perception of weights lifted by the thumb. Weights lifted by flexion feel heavier and weights lifted by extension feel lighter. 2. The change in size of the long-latency stretch reflex in flexor pollicis longus or extensor pollicis longus after thumb anaesthesia cannot explain the effect on weight perception by removal or augmentation of the background servo assistance to muscular contraction. 3. During smooth thumb flexion, thumb anaesthesia increases e.m.g. activity in flexor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis longus for any given opposing torque. 4. During smooth thumb extension the opposite occurs: e.m.g. activity in both extensor and flexor pollicis longus decreases. 5. Clamping the thumb at the proximal phalanx to limit movement solely to the interphalangeal joint reduces or abolishes the effect of anaesthesia on both weight perception and e.m.g. activity during both flexion or extension tasks. 6. Gandevia & McCloskey's findings on the distorting effects of thumb anaesthesia on weight perception cannot be used to support the hypothesis of an efferent monitoring system of the sense of effort. Our results emphasize the close functional relationship between cutaneous and joint afferent information and motor control.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIGLAND B., LIPPOLD O. C. The relation between force, velocity and integrated electrical activity in human muscles. J Physiol. 1954 Jan;123(1):214–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McCloskey D. I. Effects of related sensory inputs on motor performances in man studied through changes in perceived heaviness. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):653–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. M., Porter R. Pyramidal tract discharge in relation to movement performance in monkeys with partial anaesthesia of the movind hand. Brain Res. 1974 May 17;71(2-3):345–351. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90977-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Servo action in the human thumb. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(1):1–44. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. The sensory mechanism of servo action in human muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):521–535. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


