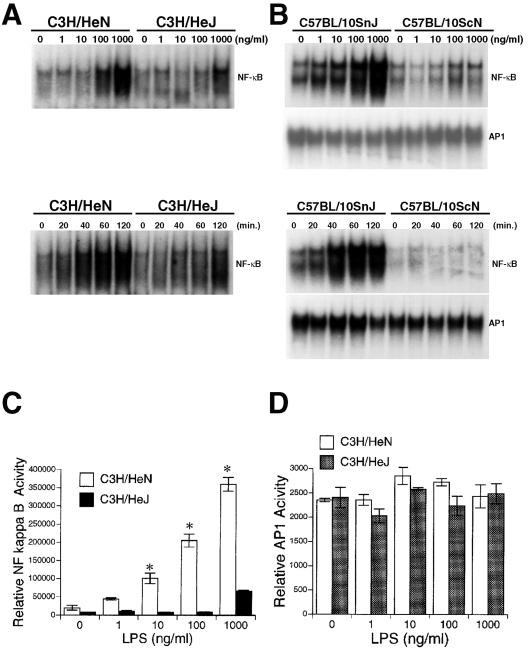
FIG. 3.
Effect of LPS on NF-κB and AP-1 binding and transcriptional activation in hepatocytes. (A) Hepatocytes from C3H/HeN, C3H/HeJ mice were treated with the indicated concentrations of LPS for 60 min or for the indicated time periods with LPS at 500 ng/ml. Nuclear extracts were prepared and the binding of nuclear proteins to a 32P-labeled NF-κB consensus oligonucleotide was analyzed by EMSA. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (B) Hepatocytes from C57BL/10SnJ, C57BL/10ScN mice were treated with the indicated concentrations of LPS for 60 min or for the indicated time periods with LPS at 500 ng/ml. Binding of nuclear proteins to a 32P-labeled NF-κB or AP-1 consensus oligonucleotide was analyzed by EMSA. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (C and D) Hepatocytes from C3H/HeN or C3H/HeJ mice on six-well plates were transiently transfected with an NF-κB (pELAM, 0.1 μg/well) or AP-1 (AP-1-luc, 0.2 μg/well) luciferase reporter vector and cotransfected with a β-galactosidase reporter vector (pIEPlacZ, 0.5 μg/well). The data (means ± SE [error bars]) shown here are a representative of six independent experiments with similar results (∗, P < 0.05 [for C3H/HeN versus C3H/HeJ]).