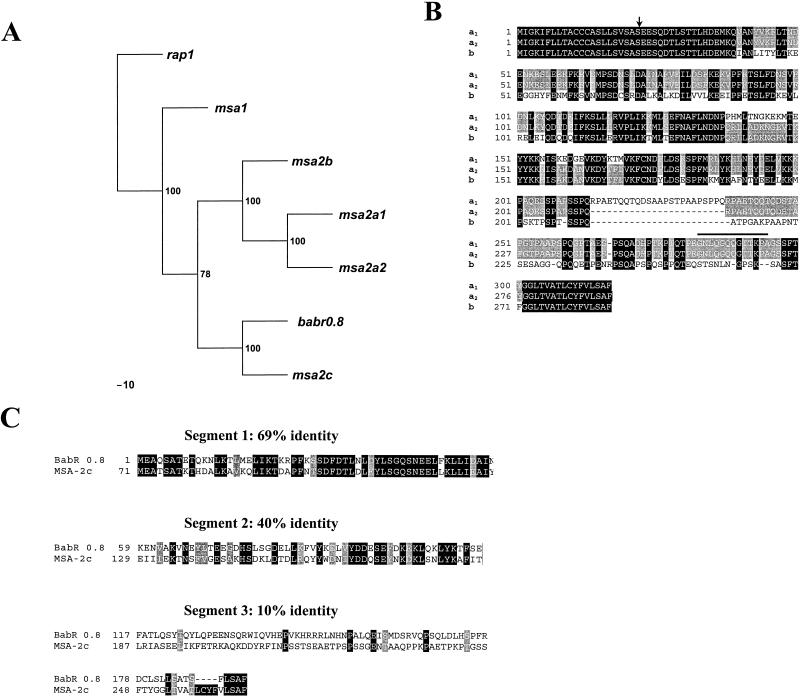
FIG. 3.
Sequence comparisons of B. bovis Mo7 msa-2 genes and encoded proteins. (A) Phylogram of the vmsa family. B. bovis rap1 is used as an outlier, and the most parsimonious tree is shown. Bootstrap values are indicated at branch points. (B) Alignment of MSA-2a1, -2a2, and -2b. Areas of amino acid identity among all three proteins are enclosed in black boxes; amino acids conserved between two of the proteins have a gray background, and variant amino acids have a white background. Deletions are indicated by dashed lines. The sequence conserved among MSA-1, -2a1, and -2a2 is indicated by a bold line above the sequence, and the predicted site for cleavage of the amino-terminal signal peptide is indicated by an arrow. (C) Fractionated alignment and sequence comparison between Mo7 MSA-2c and Australia K strain BabR 0.8. The amino acid sequences were aligned and divided into three segments according to the degree of conservation. The ORF of BabR 0.8 starts 71 aa downstream from the start codon of MSA-2c. Therefore, the region between aa 1 and 70 of MSA-2c was not included in this alignment. Areas of amino acid identity are enclosed in black boxes, conservative substitutions have a gray background, and variant amino acid substitutions have a white background.