Abstract
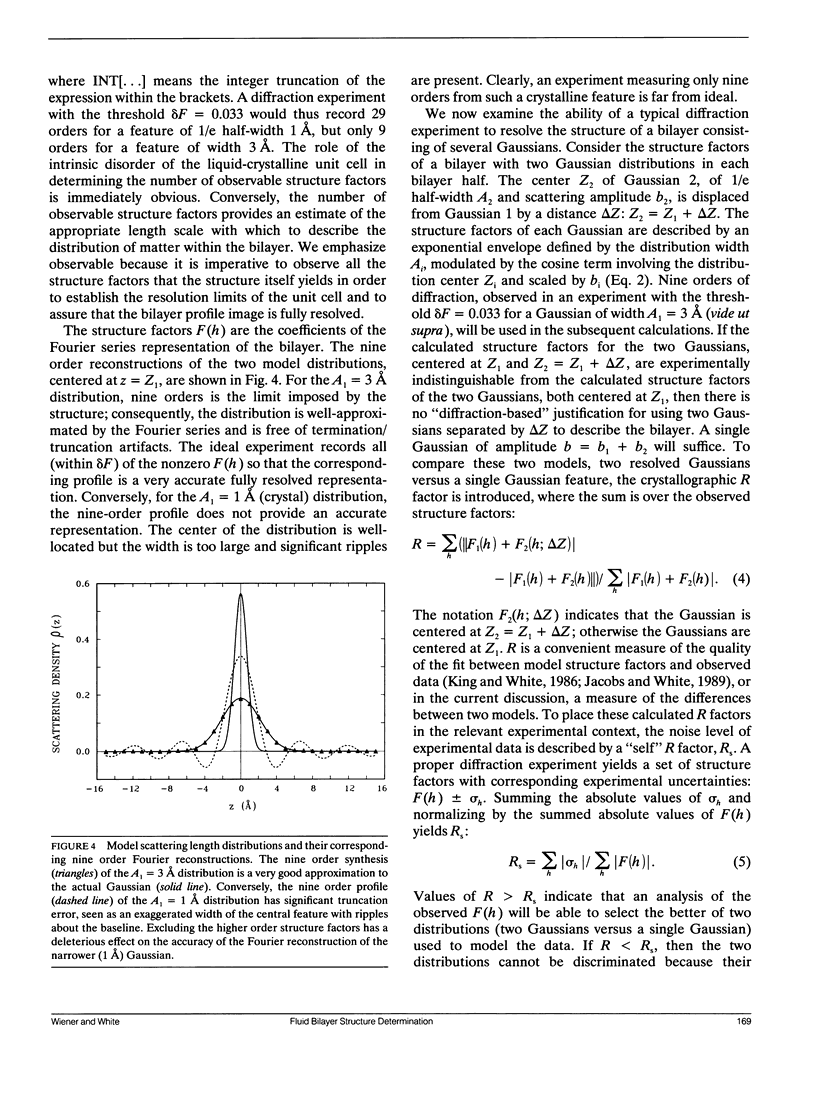
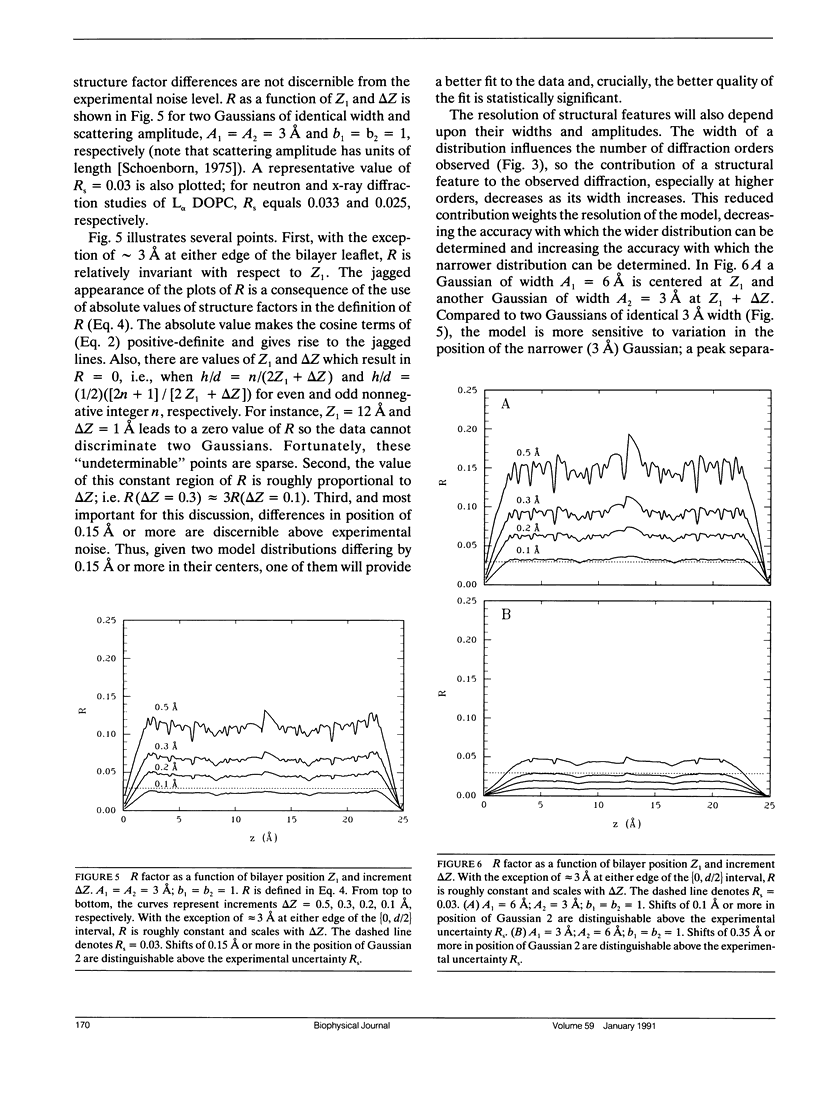
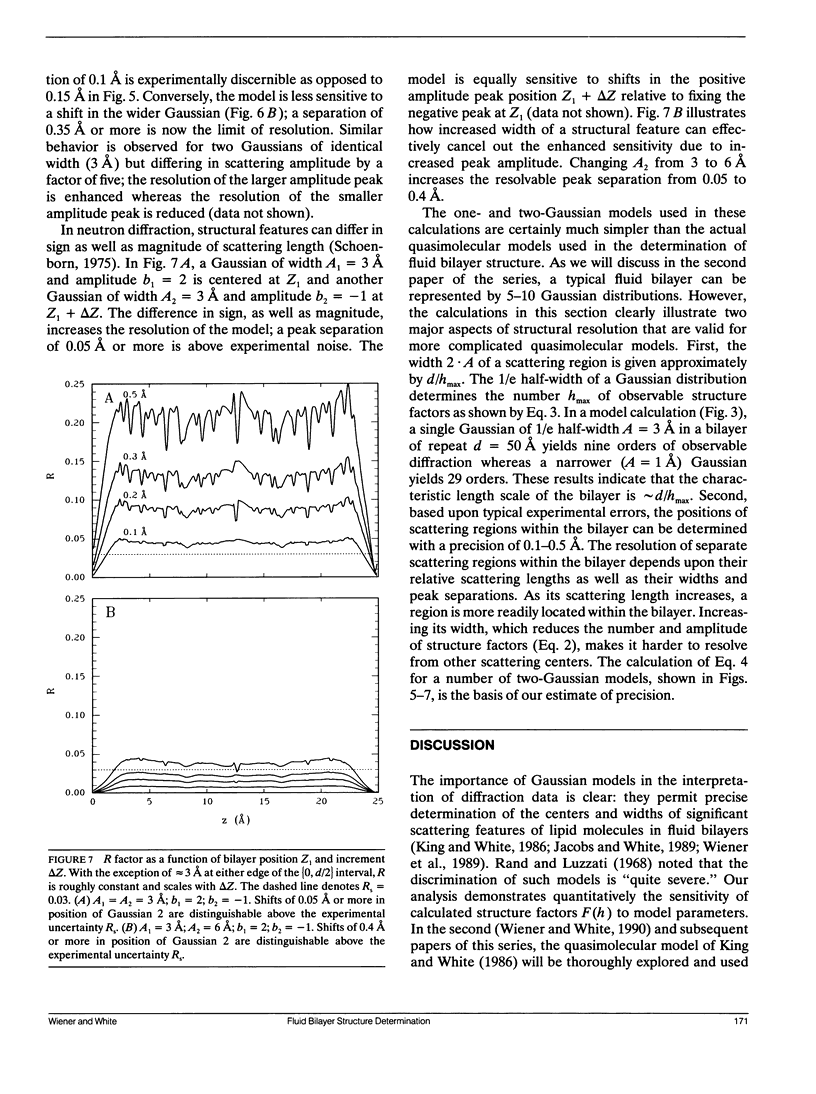
This is the first in a series of papers concerned with methods for the determination of the structures of fluid phospholipid bilayers in the liquid-crystalline (L alpha) phase. The basic approach is the joint refinement of quasimolecular models (King and White, 1986. Biophys. J. 49:1047-1054) using x-ray and neutron diffraction data. We present here (a) the rationale for quasimolecular models, (b) the nature of the resolution problem for thermally disordered bilayers, and (c) an analysis of the resolution of experiments in which Gaussian functions are used to describe the distribution of submolecular components. We show that multilamellar liquid-crystalline bilayers are best described by the convolution of a perfect lattice function with a thermally disordered bilayer unit cell. Lamellar diffraction measurements on such a system generally yield only 5-10 orders of diffraction data from which transbilayer profiles of the unit cell can be constructed. The canonical resolution of these transbilayer profiles, defined as the Bragg spacing divided by the index of the highest recorded diffraction order, is typically 5-10 A. Using simple model calculations, we show that the canonical resolution is a measure of the widths of the distributions of constituents of the unit cell rather than a measure of the spatial separation of the distributions. The widths provide a measure of the thermal motion of the bilayer constituents which can be described by Gaussian functions. The equilibrium positions of the centers of the distributions can be determined with a precision of 0.1-0.5 A based upon typical experimental errors.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaurock A. E. Evidence of bilayer structure and of membrane interactions from X-ray diffraction analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 12;650(4):167–207. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S., Raff M. C. Mammalian plasma membranes. Nature. 1975 Nov 6;258(5530):43–49. doi: 10.1038/258043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büldt G., Gally H. U., Seelig J., Zaccai G. Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. I. Head group conformation. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):673–691. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. The structure of lipid bilayers and the effects of general anaesthetics. An x-ray and neutron diffraction study. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 9;133(4):469–500. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90403-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Melchior V., Kirshner D. A., Caspar D. L. Structure of myelin lipid bilayers. Changes during maturation. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 25;155(2):133–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90441-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P. Structural analysis of hydrated egg lecithin and cholesterol bilayers. I. X-ray diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 25;100(3):345–358. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Pascher I., Pearson R. H., Sundell S. Preferred conformation and molecular packing of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 16;650(1):21–51. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. B., Mason R., Shipley G. G. Phospholipid arrangements in multilayers and artificial membranes: quantitative analysis of the X-ray diffraction data from a multilayer of 1,2-dimyristoyl-DL-phosphatidylethanolamine. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 15;94(2):297–299. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs R. E., White S. H. The nature of the hydrophobic binding of small peptides at the bilayer interface: implications for the insertion of transbilayer helices. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3421–3437. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak M. J., Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Temperature and compositional dependence of the structure of hydrated dimyristoyl lecithin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6068–6078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. I., White S. H. Determining bilayer hydrocarbon thickness from neutron diffraction measurements using strip-function models. Biophys J. 1986 May;49(5):1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83733-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyan J., Petsko G. A., Levy R. M., Karplus M. Effect of anisotropy and anharmonicity on protein crystallographic refinement. An evaluation by molecular dynamics. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):227–254. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90295-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine Y. K., Wilkins M. H. Structure of oriented lipid bilayers. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):69–72. doi: 10.1038/newbio230069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. Hydration force and bilayer deformation: a reevaluation. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4058–4066. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui T. X-ray diffraction studies of membranes. Adv Biophys. 1978;10:97–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranck J. L., Keira T., Luzzati V. A novel packing of the hydrocarbon chains in lipids. The low temperature phases of dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl-glycerol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):432–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Luzzati V. X-ray diffraction study in water of lipids extracted from human erythrocytes: the position of cholesterol in the lipid lamellae. Biophys J. 1968 Jan;8(1):125–137. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86479-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringe D., Petsko G. A. Study of protein dynamics by X-ray diffraction. Methods Enzymol. 1986;131:389–433. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)31050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenborn B. P. Advantages of neutron scattering for biological structure analysis. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1976 May;(27):110–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Cain J. E., Dratz E. A., Blasie J. K. An analysis of lamellar x-ray diffraction from disordered membrane multilayers with application to data from retinal rod outer segments. Biophys J. 1975 Dec;15(12):1201–1233. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85895-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirota E. B., Smith G. S., Safinya C. R., Plano R. J., Clark N. A. X-ray Scattering Studies of Aligned, Stacked Surfactant Membranes. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1406–1409. doi: 10.1126/science.242.4884.1406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith GS, Sirota EB, Safinya CR, Clark NA. Structure of the L beta phases in a hydrated phosphatidylcholine multimembrane. Phys Rev Lett. 1988 Feb 29;60(9):813–816. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.60.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., Suter R. M., Nagle J. F. Structure of the fully hydrated gel phase of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Biophys J. 1989 Feb;55(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82807-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Fluid bilayer structure determination by the combined use of x-ray and neutron diffraction. II. "Composition-space" refinement method. Biophys J. 1991 Jan;59(1):174–185. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82209-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcester D. L., Franks N. P. Structural analysis of hydrated egg lecithin and cholesterol bilayers. II. Neutrol diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 25;100(3):359–378. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington C. R. The interpretation of low-angle X-ray data from planar and concentric multilayered structures. The use of one-dimensional electron density strip models. Biophys J. 1969 Feb;9(2):222–234. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86381-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaccai G., Büldt G., Seelig A., Seelig J. Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. II. Chain conformation and segmental disorder. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):693–706. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]