Abstract
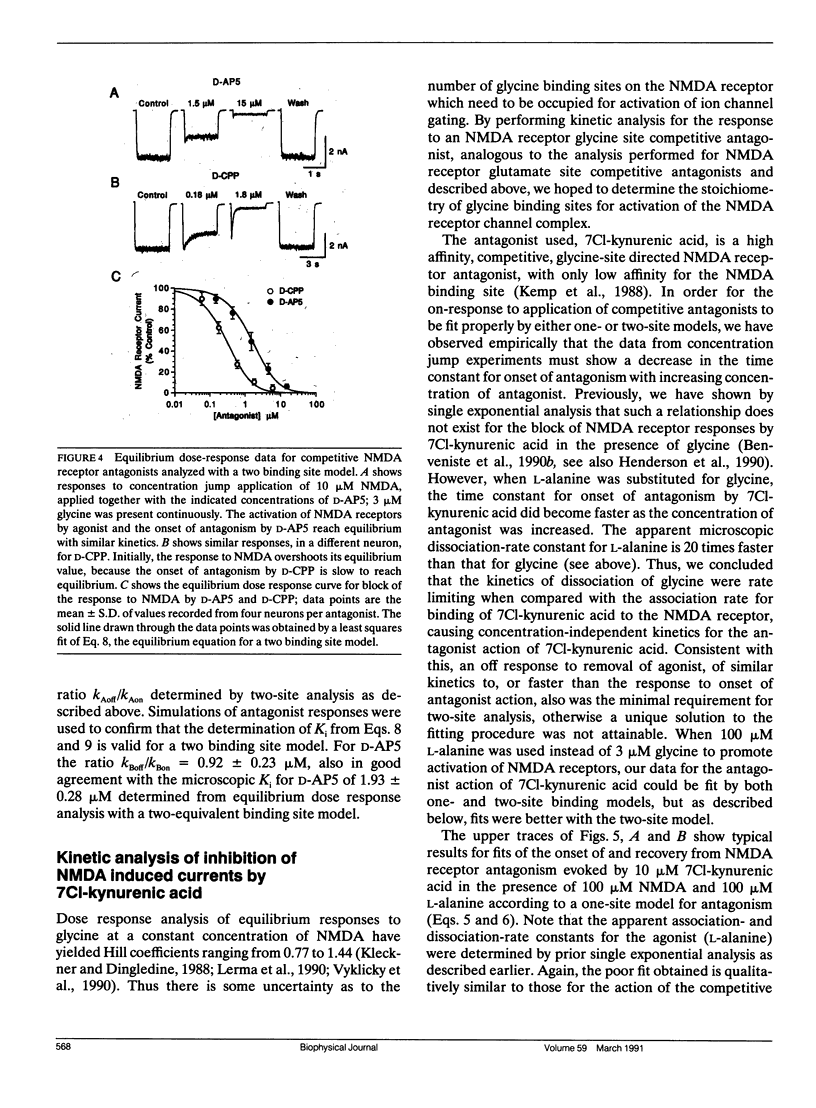
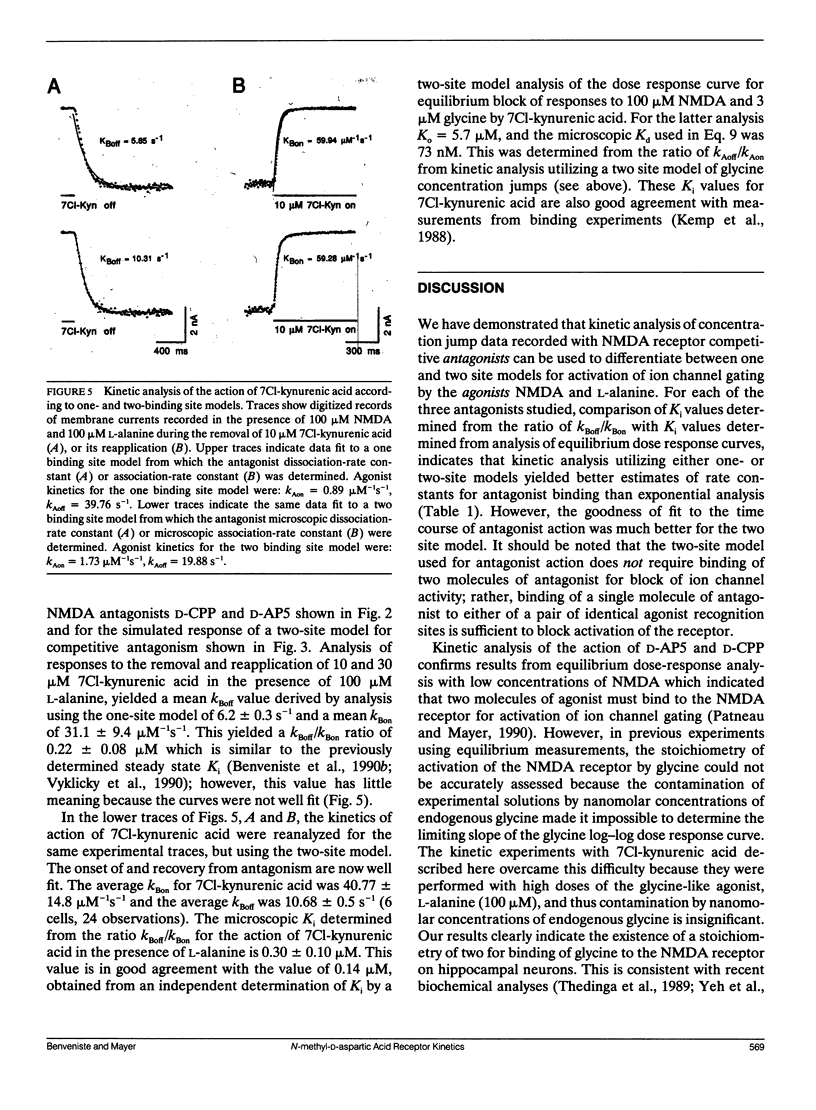
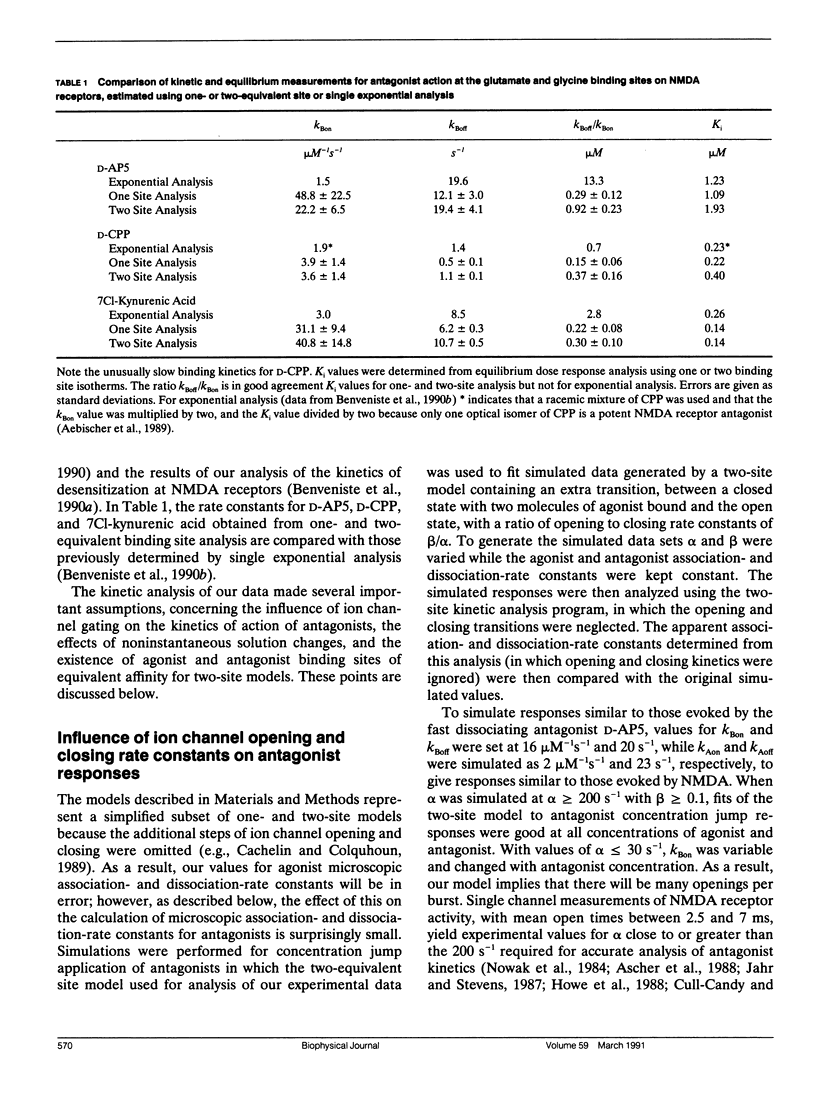
Antagonism of glutamate-receptor responses activated by N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) was studied using whole cell voltage clamp recording from mouse dissociated hippocampal neurons cultured for 10-15 d. The kinetics of onset of and recovery from NMDA receptor block during continuous application of NMDA together with either glycine, or L-alanine, were recorded in response to concentration jump application of NMDA- and glycine-binding site directed competitive antagonists, applied with a multibarrel flow pipe under conditions which allowed rapid solution changes around the cell less than 10 ms. Mathematical solutions for both one- and two-equivalent site models for competitive antagonism were determined according to the differential equations outlined by Colquhoun and Hawkes (1977. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 199:231-262). The kinetics of action of D-CPP and D-AP5, NMDA binding site antagonists, and 7Cl-kynurenic acid, a glycine binding site antagonist, were examined for each model. For all these antagonists, the kinetics for the onset of and recovery from antagonism were better fit by the two-equivalent site model, which yielded antagonist microscopic kBoff/kBon values which closely approximated Ki values determined from analysis of equilibrium dose response curves. These results suggest that two molecules of NMDA and two molecules of glycine must bind to the NMDA receptor for activation of ion channel gating.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ascher P., Nowak L. The role of divalent cations in the N-methyl-D-aspartate responses of mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:247–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. ATP-activated channels in rat and bullfrog sensory neurons: concentration dependence and kinetics. J Neurosci. 1990 Jan;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-01-00001.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste M., Clements J., Vyklický L., Jr, Mayer M. L. A kinetic analysis of the modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors by glycine in mouse cultured hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:333–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste M., Mienville J. M., Sernagor E., Mayer M. L. Concentration-jump experiments with NMDA antagonists in mouse cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Jun;63(6):1373–1384. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.6.1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachelin A. B., Colquhoun D. Desensitization of the acetylcholine receptor of frog end-plates measured in a Vaseline-gap voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:159–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Ogden D. C. Activation of ion channels in the frog end-plate by high concentrations of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:131–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Usowicz M. M. On the multiple-conductance single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in large cerebellar neurones of the rat. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:555–582. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale N., Roberts A. Dual-component amino-acid-mediated synaptic potentials: excitatory drive for swimming in Xenopus embryos. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:35–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L. Slow excitatory postsynaptic currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured mouse central neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie P. B., Brenneman D. E., Neale E. A. Morphological and biochemical differences expressed in separate dissociated cell cultures of dorsal and ventral halves of the mouse spinal cord. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 15;420(2):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Competitive antagonists and partial agonists at the glycine modulatory site of the mouse N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:189–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Davies S. N., Drejer J., Fletcher E. J., Jacobsen P., Lodge D., Nielsen F. E. Quinoxalinediones: potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):701–703. doi: 10.1126/science.2899909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huettner J. E., Baughman R. W. The pharmacology of synapses formed by identified corticocollicular neurons in primary cultures of rat visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1988 Jan;8(1):160–175. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-01-00160.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of NMDA receptor-channel kinetic behavior. J Neurosci. 1990 Jun;10(6):1830–1837. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-06-01830.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp J. A., Foster A. C., Leeson P. D., Priestley T., Tridgett R., Iversen L. L., Woodruff G. N. 7-Chlorokynurenic acid is a selective antagonist at the glycine modulatory site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6547–6550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. W., Dingledine R. Requirement for glycine in activation of NMDA-receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):835–837. doi: 10.1126/science.2841759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krouse M. E., Lester H. A., Wassermann N. H., Erlanger B. F. Rates and equilibria for a photoisomerizable antagonist at the acetylcholine receptor of Electrophorus electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Aug;86(2):235–256. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerma J., Zukin R. S., Bennett M. V. Glycine decreases desensitization of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes and is required for NMDA responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2354–2358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. A., Clements J. D., Westbrook G. L., Jahr C. E. Channel kinetics determine the time course of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):565–567. doi: 10.1038/346565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Vyklicky L., Jr, Clements J. Regulation of NMDA receptor desensitization in mouse hippocampal neurons by glycine. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):425–427. doi: 10.1038/338425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBain C. J., Kleckner N. W., Wyrick S., Dingledine R. Structural requirements for activation of the glycine coagonist site of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;36(4):556–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Olverman H. J., Nguyen L., Watkins J. C., Cotman C. W. Two classes of N-methyl-D-aspartate recognition sites: differential distribution and differential regulation by glycine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9836–9840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Structure-activity relationships for amino acid transmitter candidates acting at N-methyl-D-aspartate and quisqualate receptors. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2385–2399. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02385.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thedinga K. H., Benedict M. S., Fagg G. E. The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor complex: a stoichiometric analysis of radioligand binding domains. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Sep 25;104(1-2):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Kleckner N. W., Dingledine R. N-methyl-D-aspartate/glycine and quisqualate/kainate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes: antagonist pharmacology. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;35(3):360–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyklický L., Jr, Benveniste M., Mayer M. L. Modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor desensitization by glycine in mouse cultured hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:313–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh G. C., Bonhaus D. W., McNamara J. O. Evidence that zinc inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-gated ion channel activation by noncompetitive antagonism of glycine binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;38(1):14–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


