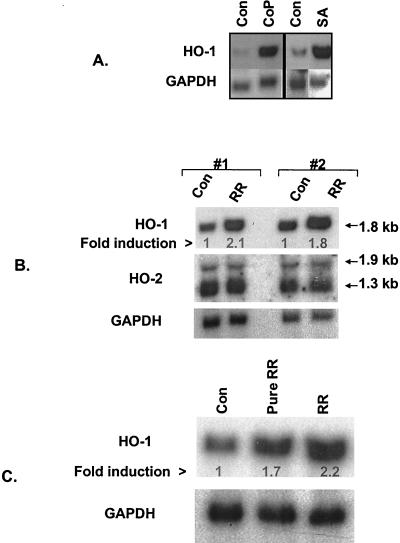
FIG. 1.
Induction of endothelial HO-1 expression by known inducers and R. rickettsii infection. (A) Northern blot analysis of RNA from EC treated with cobalt protoporphyrin (CoP; 50 μM for 18 h) or sodium arsenite (SA; 50 μM for 3 h). Control lanes (Con) contain RNA from cells incubated with the culture medium alone. Total RNA (10 μg per lane) was electrophoresed, transferred to nylon membrane, and hybridized with a 32P-labeled human HO-1 cDNA probe. The membrane was stripped and reprobed with a human GAPDH probe to control for loading and transfer. (B) Analysis of HO-1 and HO-2 expression during R. rickettsii infection of EC. Two sets of RNA prepared from uninfected (Con) and 4-h R. rickettsii infected (RR) EC were hybridized with human HO-1, HO-2, and GAPDH probes, respectively. The positions of the transcripts for isozymes of HO are indicated by arrows. The fold induction was calculated relative to the control level for each condition, which was assigned a value of 1. (C) Comparison of HO-1 induction response in EC infected with stock versus partially purified R. rickettsii. Lane Pure RR shows HO-1 level in EC infected for 4 h with 1.5 × 104 PFU/cm2 of a sucrose-renografin density gradient-purified R. rickettsii preparation. Lane RR shows HO-1 induction obtained with a 6.0 × 104 PFU/cm2 preparation of R. rickettsii isolated as a lysate of Vero cells in the same experiment. The fold induction was calculated relative to the basal level of HO-1 expression in uninfected EC (lane 1).