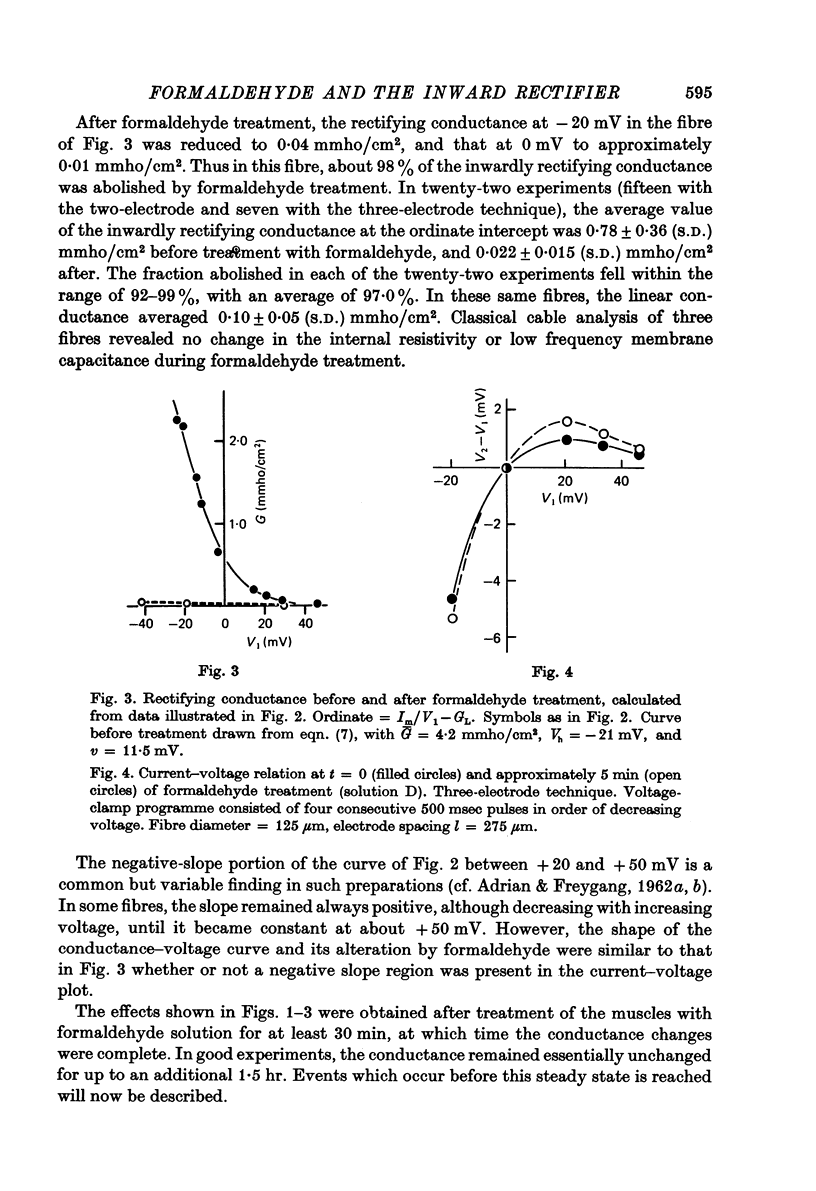
Abstract
1. The inwardly rectifying potassium conductance of the membrane of frog sartorius muscle fibres is greatly reduced by treatment of muscles for 30 min with a solution containing formaldehyde (10 mM). 2. A transient increase in the conductance of the inward rectifier is observed early during formaldehyde action. 3. Analysis of the biphasic time course of the conductance changes, as determined under controlled voltage conditions, suggests that treatment with formaldehyde alters simultaneously, but in opposite ways, two factors that determine the conductance of the inward rectifier. 4. The linear component of the current-voltage relation, which dominates the relation at strongly positive potentials, is not affected while the above changes occur. But on prolonged exposure to formaldehyde the leak conductance increases. 5. The effects of formaldehyde on the inward rectifier are reversible on prolonged superfusion with normal Ringer solution. 6. The slight inward rectification remaining after most of the extracellular K is replaced by Rb, is similarly reduced by treatment with formaldehyde. 7. The results are interpreted in terms of the chemical properties of formaldehyde and present views of the mechanisms of inward rectification.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H., FREYGANG W. H. Potassium conductance of frog muscle membrane under controlled voltage. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163:104–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADRIAN R. H. THE RUBIDIUM AND POTASSIUM PERMEABILITY OF FROG MUSCLE MEMBRANE. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:134–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Slow changes in potassium permeability in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):645–668. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H. Rectification in muscle membrane. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1969;19(2):339–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W. The decline of potassium permeability during extreme hyperpolarization in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;225(1):57–83. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argibay J. A., Hutter O. F., Slack J. R. Consecutive activation and inactivation of the delayed rectifier in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):46P–47P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole K. S., Curtis H. J. MEMBRANE POTENTIAL OF THE SQUID GIANT AXON DURING CURRENT FLOW. J Gen Physiol. 1941 Mar 20;24(4):551–563. doi: 10.1085/jgp.24.4.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The effect of sudden changes in ionic concentrations on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:370–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F., NOBLE D. The chloride conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:89–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Krasne S., Ciani S. Anomalous permeabilities of the egg cell membrane of a starfish in K+-Tl+ mixtures. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Sep;70(3):269–281. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.3.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. The anomalous rectification and cation selectivity of the membrane of a starfish egg cell. J Membr Biol. 1974;18(1):61–80. doi: 10.1007/BF01870103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. The effect of diameter on the electrical constants of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):105–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter O. F. Potassium conductance of skeletal muscle treated with formaldehyde. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1215–1217. doi: 10.1038/2241215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SJODIN R. A. Rubidium and cesium fluxes in muscle as related to the membrane potential. J Gen Physiol. 1959 May 20;42(5):983–1003. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.5.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The differential effects of tetraethylammonium and zinc ions on the resting conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):231–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


