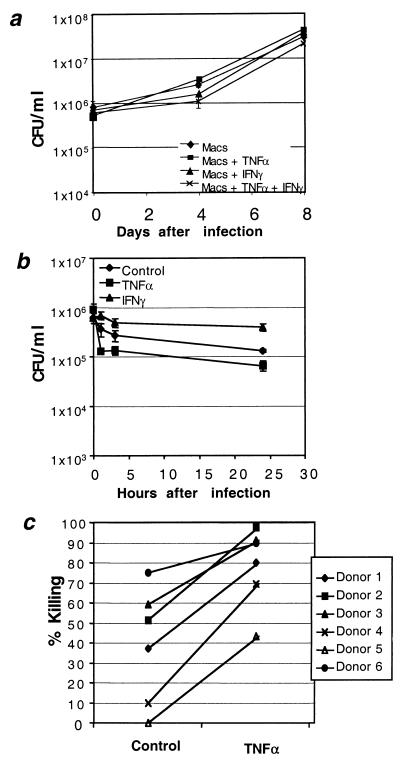
FIG. 2.
Effect of human neutrophils on the viability of intracellular M. tuberculosis. (a) Time course of M. tuberculosis viability after infection of macrophages treated with medium only (♦) or 100 U of recombinant human TNF-α (rhTNF-α) (▪)/ml or 100 U of rhIFN-γ (▴)/ml or both (×). Results presented are from a single anonymous donor who was representative of over 30 examined. Data points represent three separate infections. CFU for each data point were calculated as the average count from four plates at two different dilutions. (b) Time course of M. tuberculosis viability after infection of neutrophils treated with medium only (♦), 100 U of rhTNF-α (▪)/ml, or 100 U of rhIFN-γ (▴)/ml. Results were obtained from a single anonymous donor. Data points represent three separate infections. CFU for each data point were calculated as the average count from four plates at two different dilutions. (c) Donor-to-donor neutrophil variation in spontaneous and TNF-α-stimulated killing of intracellular M. tuberculosis 24 h after infection. Percent killing relative to time zero (immediately after washout of uningested organisms) for each donor with and without 100 U of rhTNF-α/ml was calculated from three separate infections performed in parallel. All donors exhibited a significant increase in killing in response to TNF-α (P < 0.01; Student's t test).