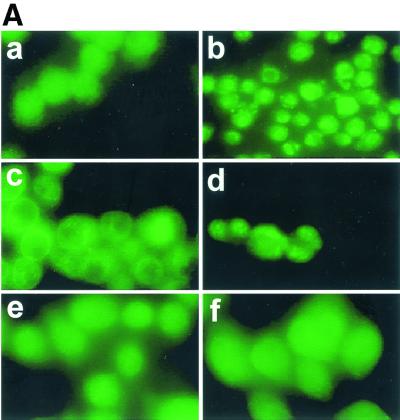
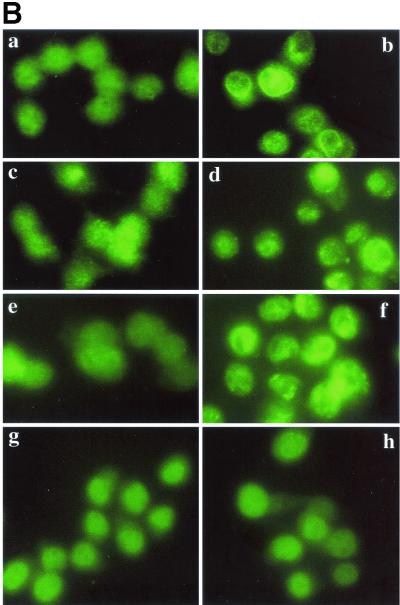
FIG. 1.
Translocation of PKC δ after infection with L. monocytogenes or pretreatment with PMA. J774 cells were infected with different strains of L. monocytogenes or the same volume of PBS for 45 s and then processed for immunofluorescence analysis as described in the text. (A) Panel a, uninfected cells; panel b, uninfected cells treated with PMA (100 nM) for 10 min; panels c and d, cells infected with the wild type (PKC δ translocation is indicated by a bright green ring around the periphery of a cell [panel c] or by discrete bright round areas which appear to be clusters near the periphery of a cell [panel d]); panel e, cells infected with the LLO mutant strain; panel f, cells infected with the PI-PLC mutant strain. (B) Effects of inhibitors on translocation of PKC δ. PBS, SK&F 96365 (25 μM), hispidin (5 μM), or rottlerin (25 μM) was added to J774 cells 30 min prior to infection with the wild type. Uninfected cells to which PBS or inhibitor was added 30 min prior to infection are shown in the left panel of each row. Control or inhibitor-treated cells infected with the wild type for 45 s are shown in the right panel of each row. Panels a and b, control; panels c and d, cells pretreated with SK&F 96365; panels e and f, cells pretreated with hispidin; panels g and h, cells pretreated with rottlerin.