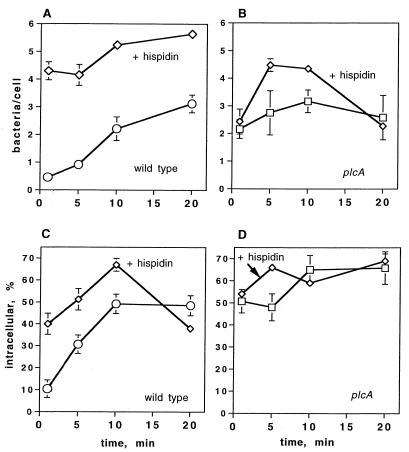
FIG. 7.
Effects of hispidin on association of L. monocytogenes with J774 cells and entry of L. monocytogenes into J774 cells. (A) Association of the wild type with untreated J774 cells (○) or cells pretreated with hispidin (5 μM) (⋄). (B) Association of the PI-PLC mutant with untreated J774 cells (□) or cells pretreated with hispidin (5 μM) (⋄). (C) Percentage of associated wild-type bacteria that were internalized in untreated J774 cells (○) or cells pretreated with hispidin (5 μM) (⋄). (D) Percentage of associated PI-PLC mutant bacteria that were internalized in untreated J774 cells (□) or cells pretreated for 30 min with hispidin (5 μM) (⋄). The total number of bacteria associated with the J774 cells was calculated as follows: total number of FITC-labeled bacteria (green)/total number of cells per image. The results are expressed as averages ± standard errors of the means for three sets of experiments in which a total of 200 to 250 J774 cells were counted. For association of the wild type in cells treated with hispidin P < 0.05 at 1, 5, and 10 min compared to the association for untreated cells. The percentage of internalized bacteria was calculated as described in the text. The results are expressed as averages ± standard errors of the means for three sets of experiments in which a total of 200 to 250 J774 cells were counted. For the percentage of internalized wild-type bacteria in cells treated with hispidin P < 0.05 compared to the percentage for untreated cells at 1, 5, and 10 min.