Abstract
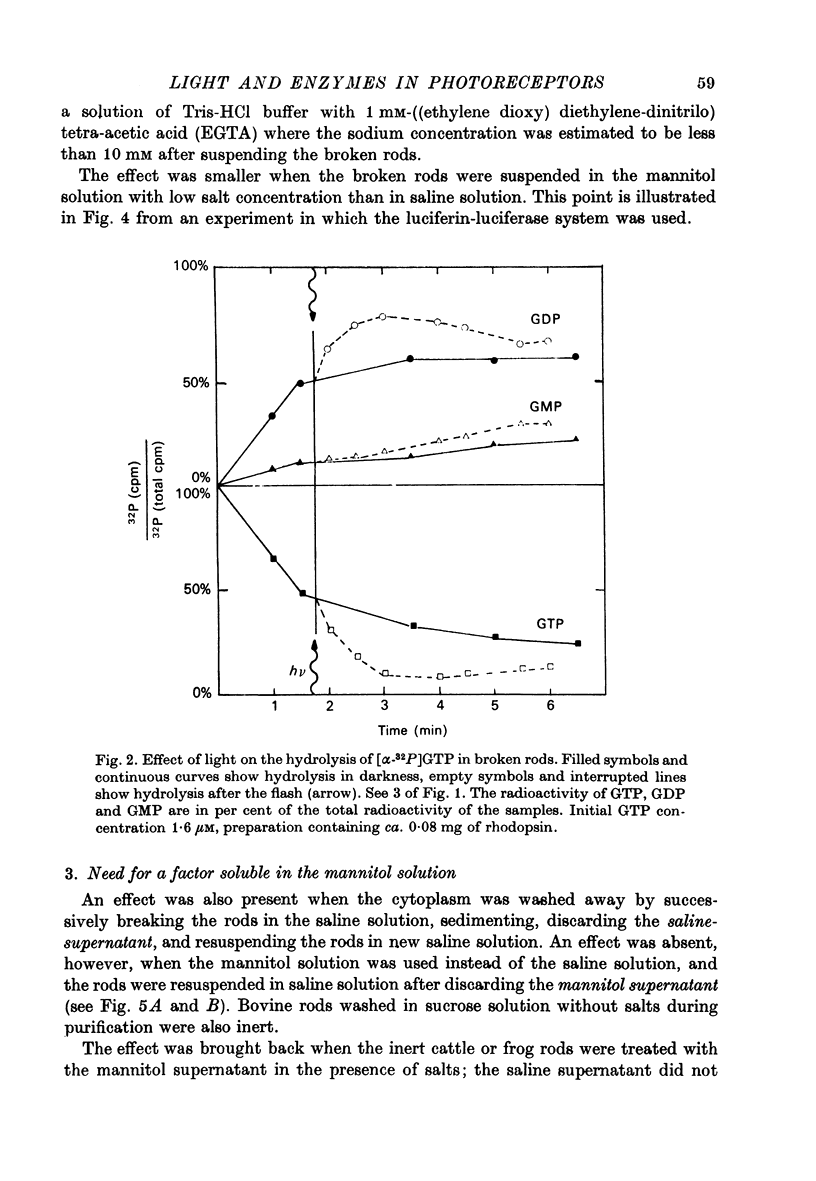
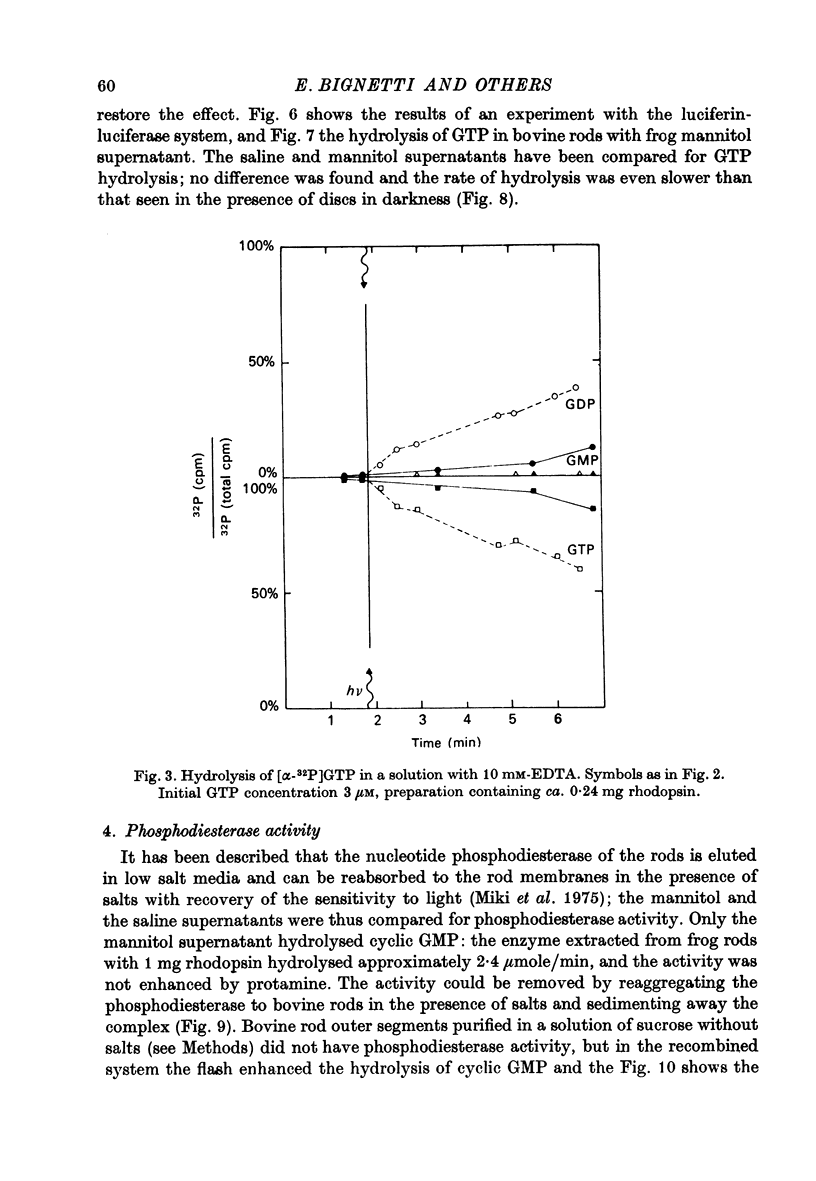
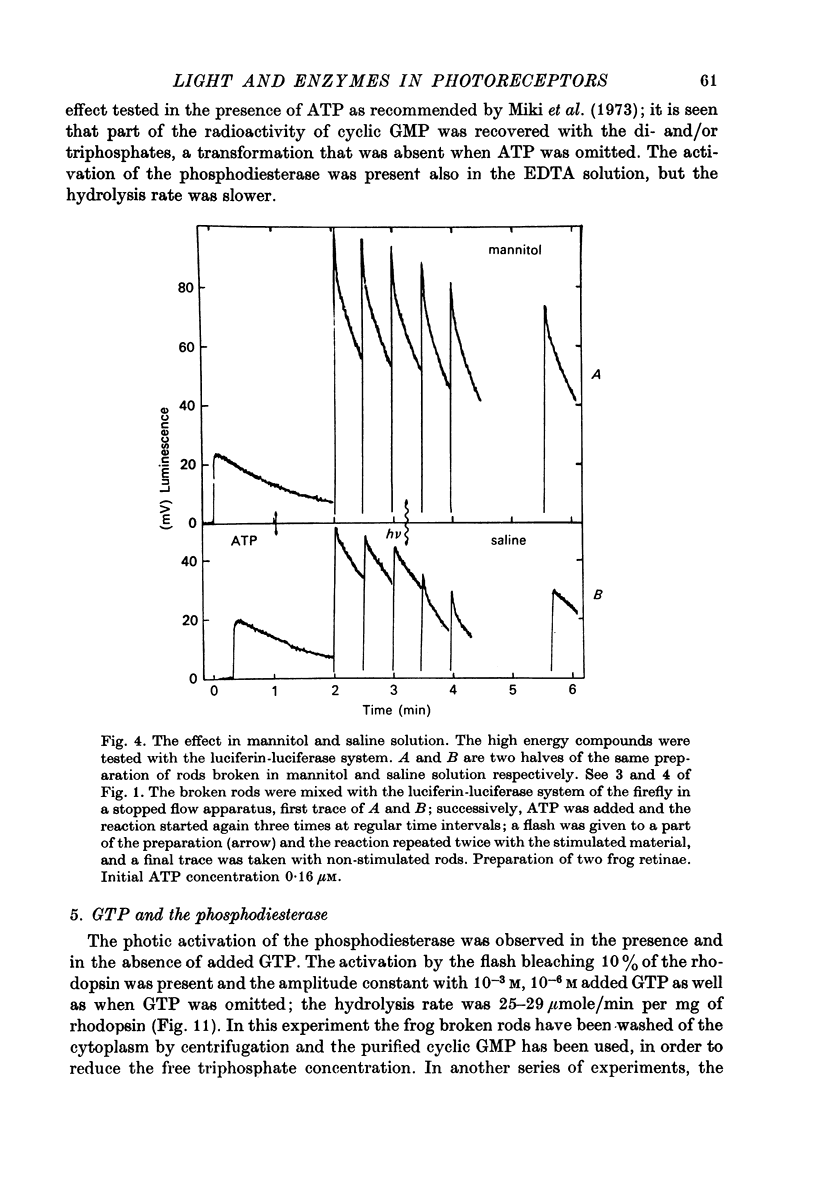
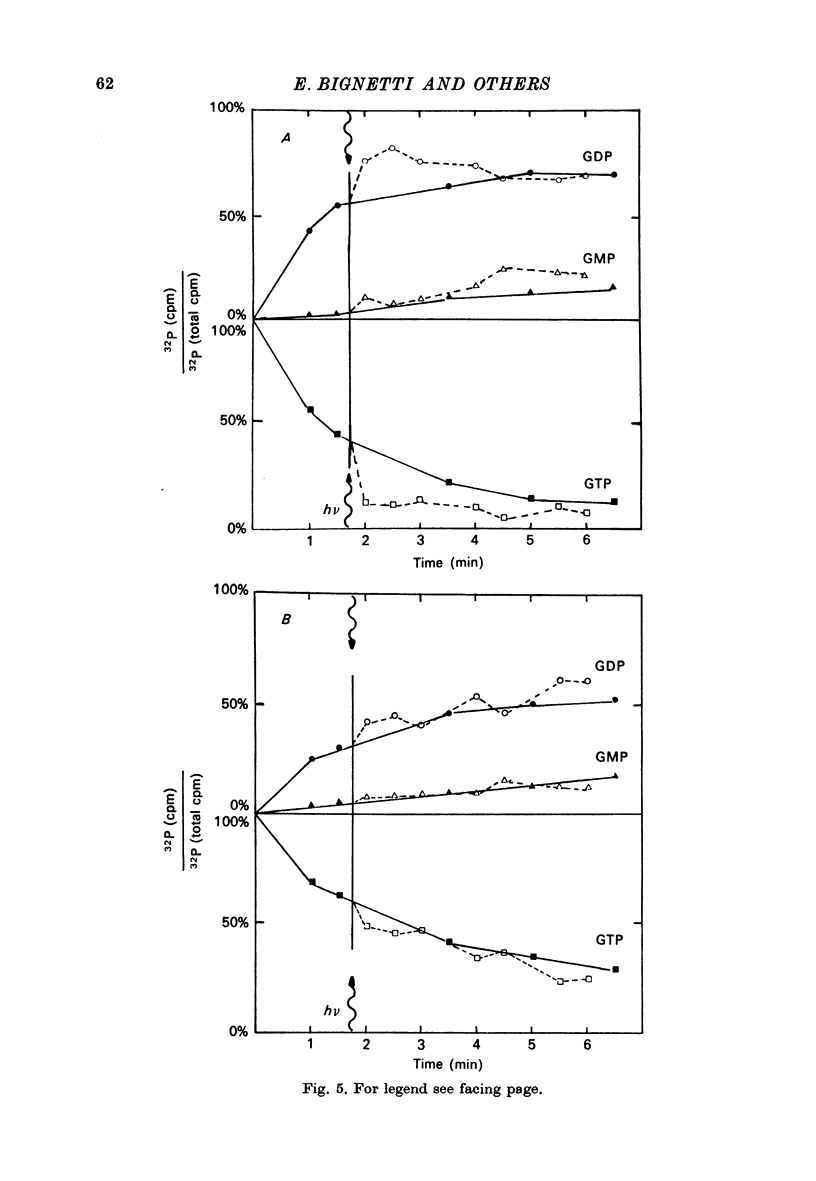
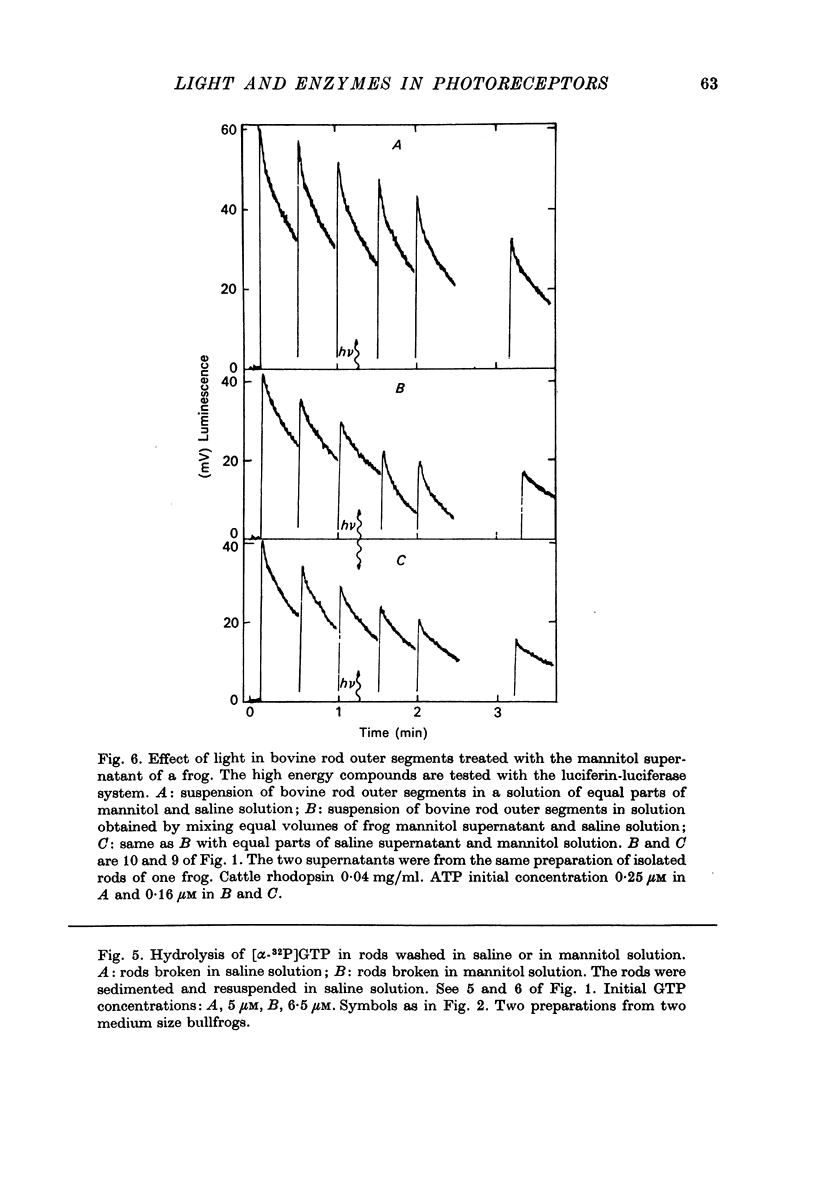
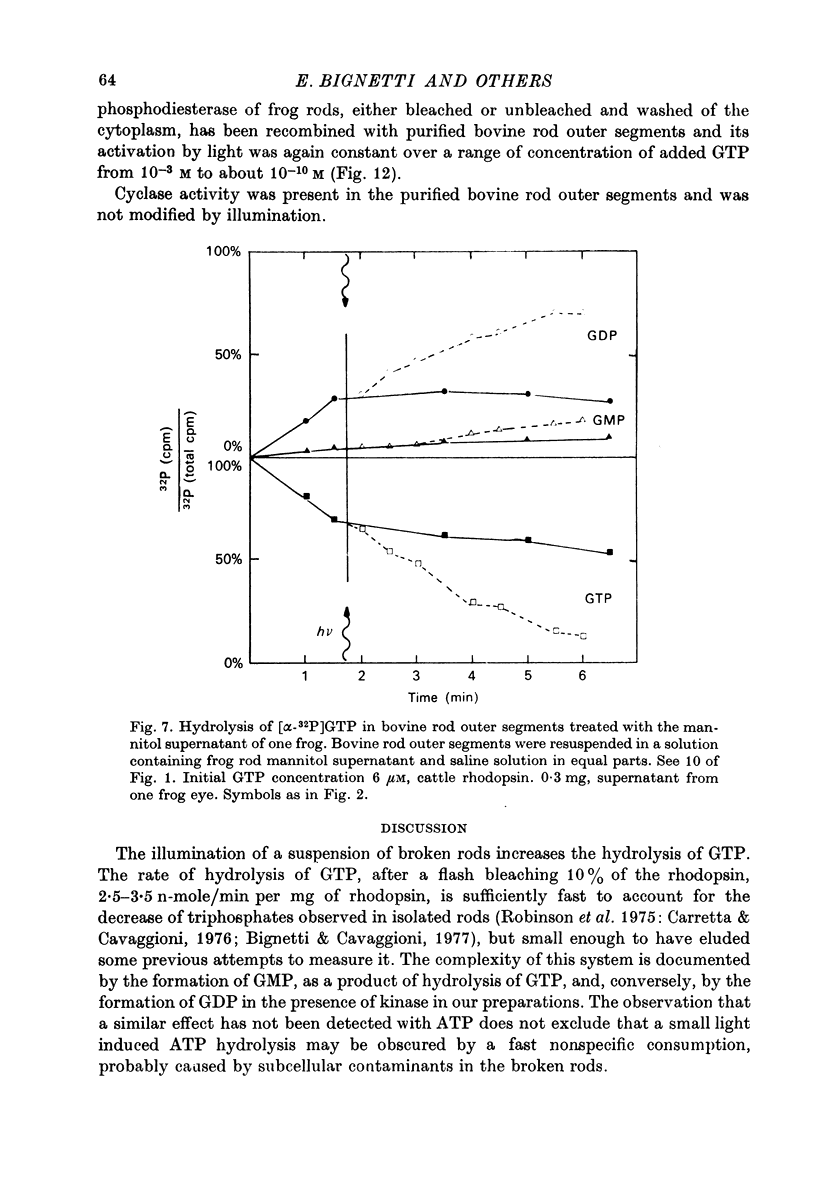
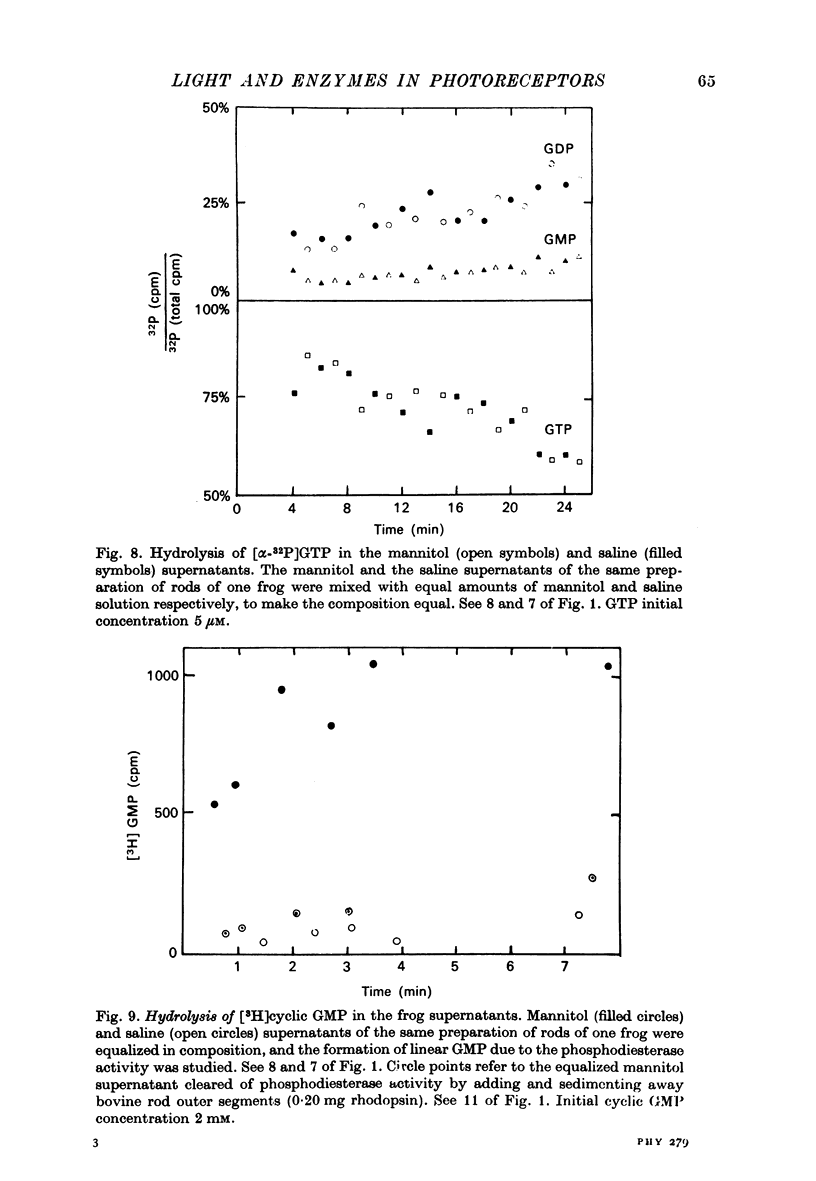
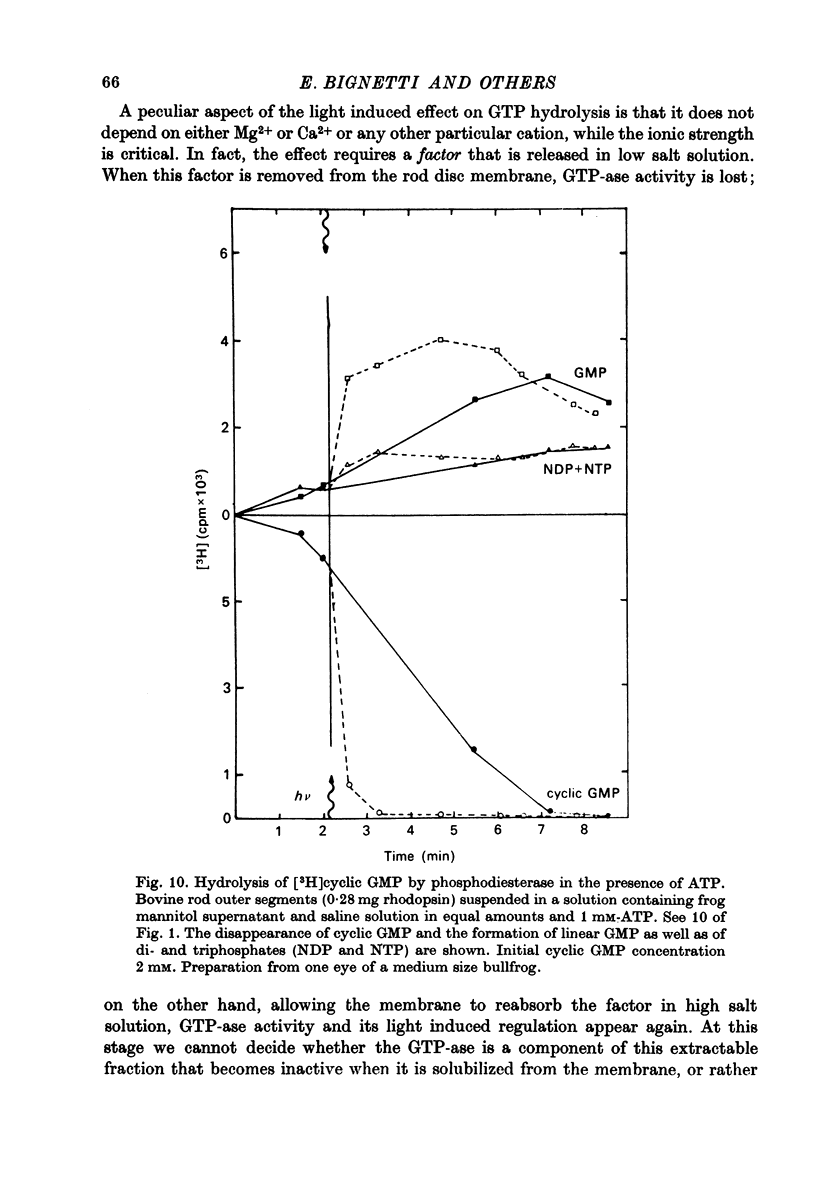
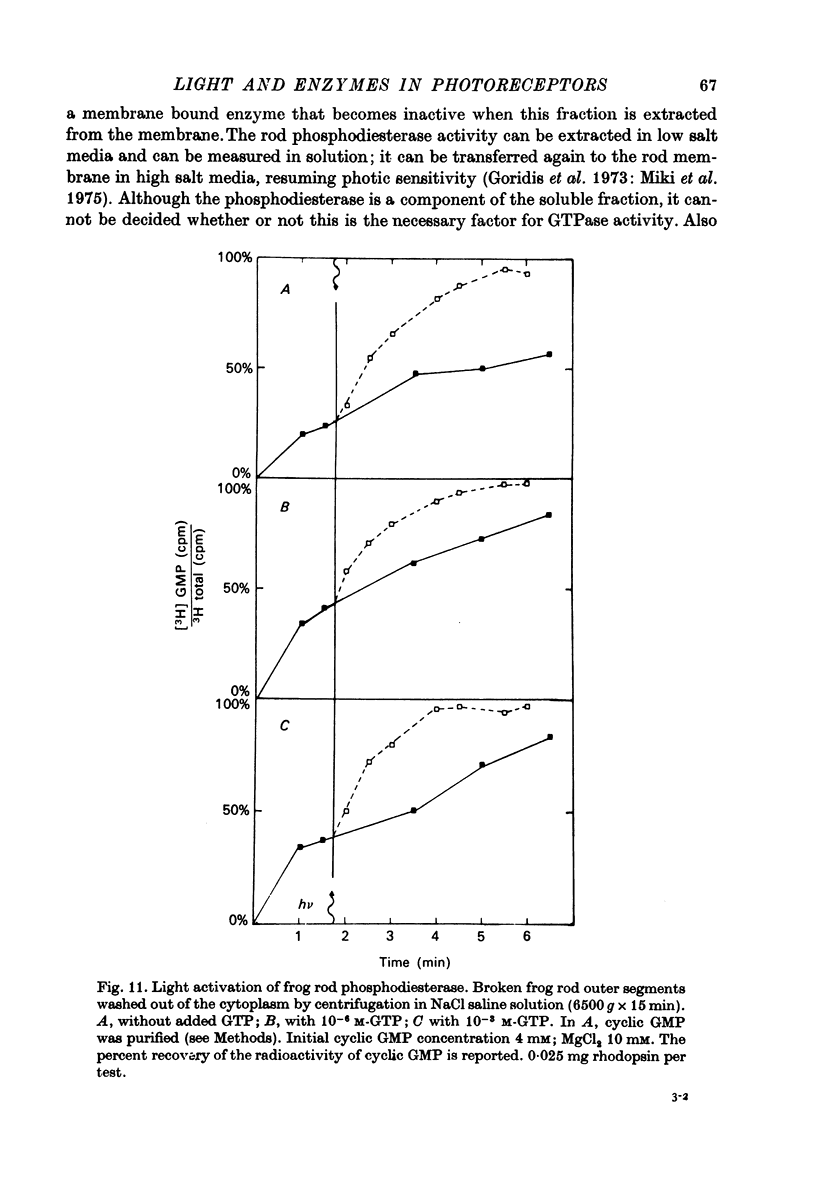
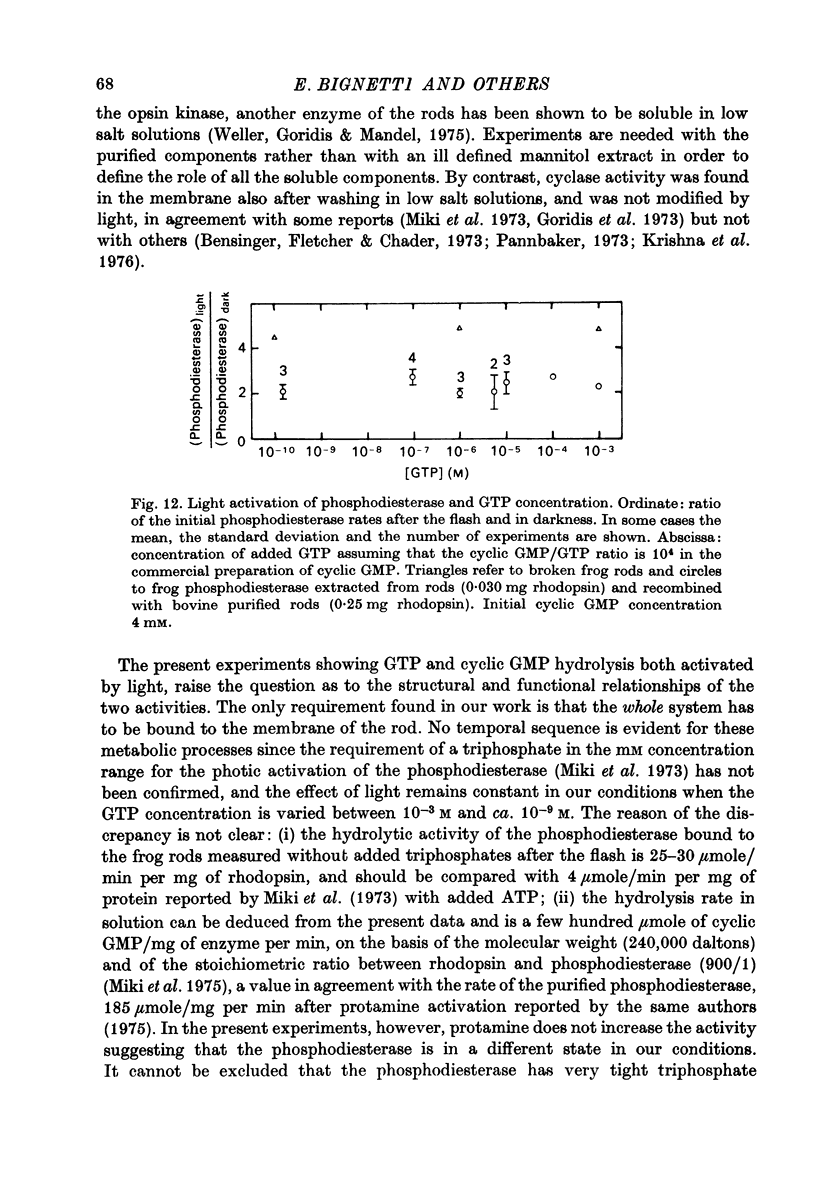
1. The hydrolysis of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and the consequent formation of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and phosphate (P1) are activated by light in a suspension of broken retinal rods: the hydrolysis rate with GTP in the micrometer concentration range is 2.5-3.5 n-mole/min per mg of rhodopsin in the preparation. 2. The ionic composition of the medium suspending the rods is not critical: the hydrolysis is present in NaCl saline solution with MG2+ as well as in Tris-HC1 buffer solution, and with the chelating agent EDTA. 3. The ionic strength is critical: the effect is reduced when the broken rods are suspended in a low salt mannitol solution, and is altogether abolished when they are separated from the mannitol solution; it reappears when the mannitol solution is added again in the presence of salts. An element essential for the effect is thus reversibly released in the mannitol solution. No hydrolytic activity on GTP, however, is found in the mannitol soluble fraction. 4. The cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase is eluted from the rods in the mannitol solution, and is reaggregated to the rods in the presence of salts; once recombined with the rods, it can be activated by light. 5. The activation of the phosphodiesterase by light is present in the absence of added nucleotide triphosphates.
Full text
PDF

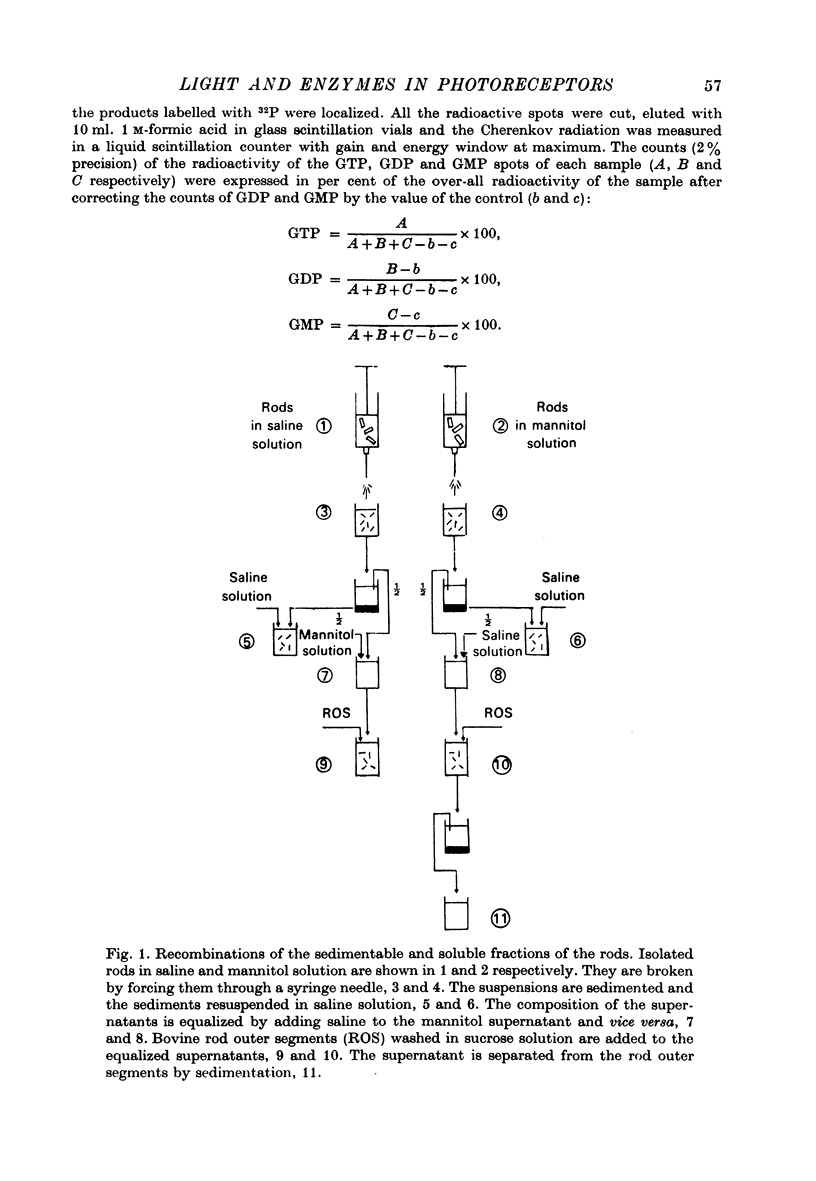


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensinger R. E., Fletcher R. T., Chader G. J. Guanylate cyclase: inhibition by light in retinal photoreceptors. Science. 1974 Jan 11;183(4120):86–87. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4120.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignetti E., Cavaggioni A. Metabolism of the frog outer segments: a kinetic study. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):705–717. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretta A., Cavaggioni A. On the metabolism of the rod outer segments. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;257(3):687–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daemen F. J. Vertebrate rod outer segment membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 28;300(3):255–288. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goridis C., Virmaux N., Urban P. F., Mandel P. Guanyl cyclase in a mammalian photoreceptor. FEBS Lett. 1973 Mar 1;30(2):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Krishnan N., Fletcher R. T., Chader G. Effects of light on cyclic GMP metabolism in retinal photoreceptors. J Neurochem. 1976 Sep;27(3):717–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb10399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki N., Baraban J. M., Keirns J. J., Boyce J. J., Bitensky M. W. Purification and properties of the light-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase of rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6320–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki N., Keirns J. J., Marcus F. R., Freeman J., Bitensky M. W. Regulation of cyclic nucleotide concentrations in photoreceptors: an ATP-dependent stimulation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase by light. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3820–3824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannbacker R. G. Control of guanylate cyclase activity in the rod outer segment. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1138–1140. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Lin M. C., Londos C., Rendell M., Rodbell M. The hepatic adenylate cyclase system. I. Evidence for transition states and structural requirements for guanine nucloetide activiation. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4239–4245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Virmaux N., Mandel P. Light-stimulated phosphorylation of rhodopsin in the retina: the presence of a protein kinase that is specific for photobleached rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler G. L., Matuto Y., Bitensky M. W. Light-activated GTPase in vertebrate photoreceptors. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):822–824. doi: 10.1038/269822a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman W. F., Daemen F. J., Bonting S. L. Distribution of enzyme activities in subcellular fractions of bovine retina. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4700–4705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


