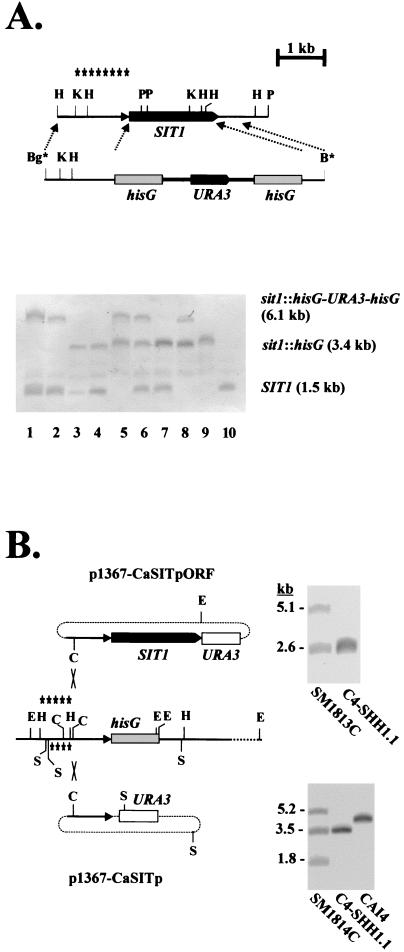
FIG. 1.
Disruption of SIT1. (A) The wild-type genomic structure of SIT1 and the disruption fragment containing the URA blaster module (hisG-URA3-hisG) are shown (top). The relevant diagnostic restriction sites at the examination of the genomic configuration of SIT1 are HindIII (H), KpnI (K), and PvuII (P); the BglII (Bg*) and BamHI (B*) sites at the ends of the disruption fragment were generated by PCR. Asterisks indicate the region used as a probe in the Southern blot (bottom). Genomic DNAs of the following strains were digested by KpnI and PvuII and analyzed by Southern blotting: C4-SB1 (lane 1)and C4-SB4 (lane 2) (SIT1/sit1Δ::hisG-URA3-hisG); C4-SH1.1 (lane 3) and C4-SH4.1 (lane 4) (SIT1/sit1Δ::hisG); C4-SHB1.1 (lane 5) (sit1Δ::hisG-URA3-hisG/sit1Δ::hisG); C4-SHB4.21 (lane 6) (SIT1/sit1Δ::hisG-URA3-hisG/sit1Δ::hisG); C4-SHH4/21-VII (lane 7) (SIT1/sit1Δ::hisG/sit1Δ::hisG); C4-SHHB4/21-VII (lane 8) (sit1Δ::hisG-URA3-hisG/sit1Δ::hisG/sit1Δ::hisG); C4-SHHH4/21-VII (lane 9) (sit1Δ::hisG/sit1Δ::hisG/sit1Δ::hisG); and CAI4 (lane 10) (SIT1/SIT1). (B) Strategy to reconstitute the SIT1 gene in the sit1 mutant C4-SHH1.1. Plasmid p1367-CaSITpORF was cut with ClaI (C) and integrated into the SIT1 promoter region by homologous recombination. As a control, plasmid p1367-CaSITp was integrated similarly. The diagnostic restriction sites used in Southern blots were EheI (E) and SspI (S); the respective probes for the plasmids are indicated above and below the sit1 region. Examples of Southern blots verifying correct integrations are shown next to the respective plasmids (see Materials and Methods).