Abstract
1. The coincident release of renin and lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) from rat renal cortical tissue slices was studied during calcium depletion, metabolic inhibition, and with the addition of ouabain (1 mM) to the incubation medium.
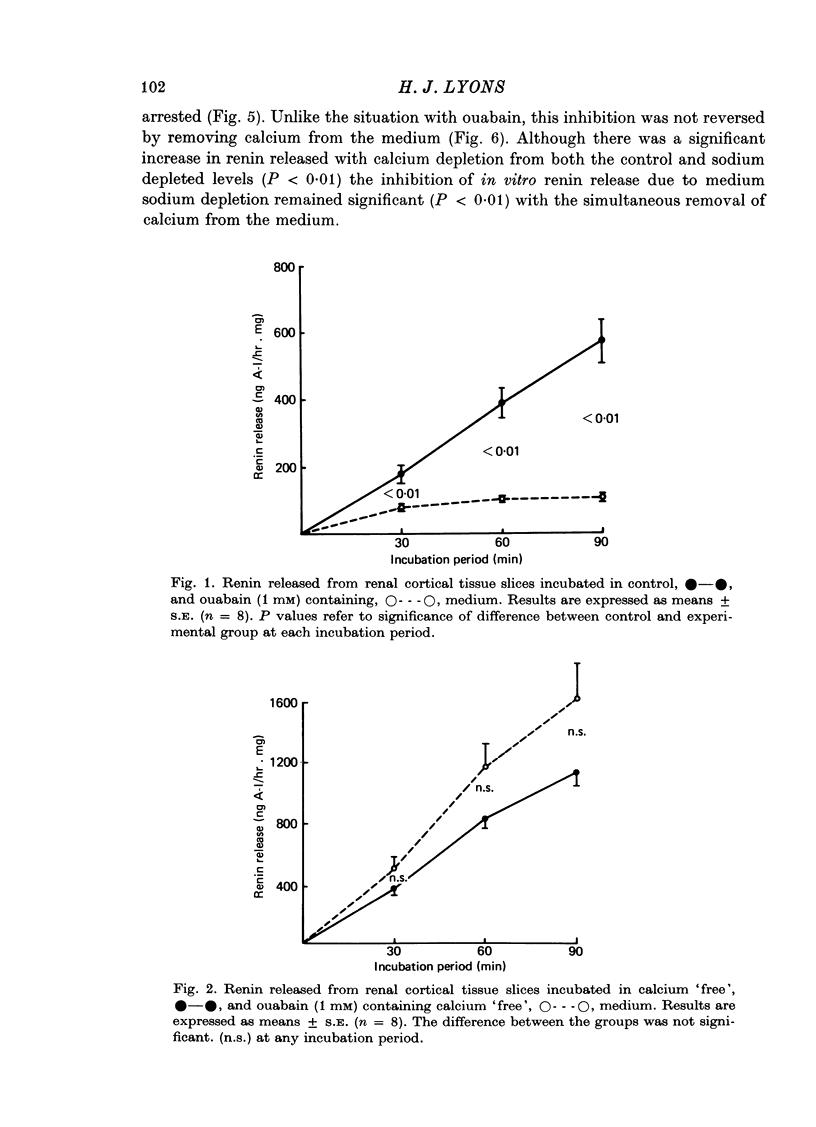
2. The results indicate that although LDH accumulated in the medium during incubation, the pattern was dissimilar to that of renin. Ouabain significantly inhibited renin release in calcium containing medium, but had no effect on LDH release. Renin release was potentiated in calcium `free' media, while calcium depletion reduced the release of LDH.
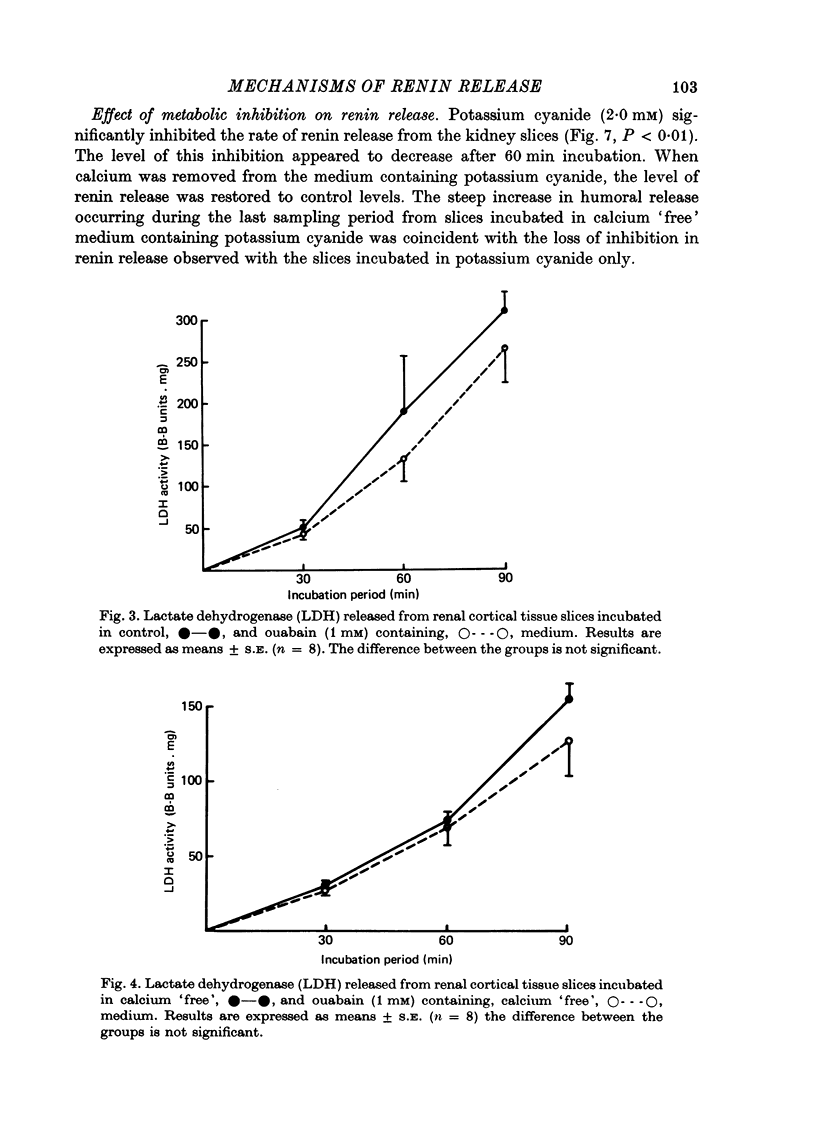
3. The addition of potassium cyanide (2 mM) significantly inhibited the release of renin from these tissue slices. Cyanide was ineffective, however, when administered in calcium `free' medium.
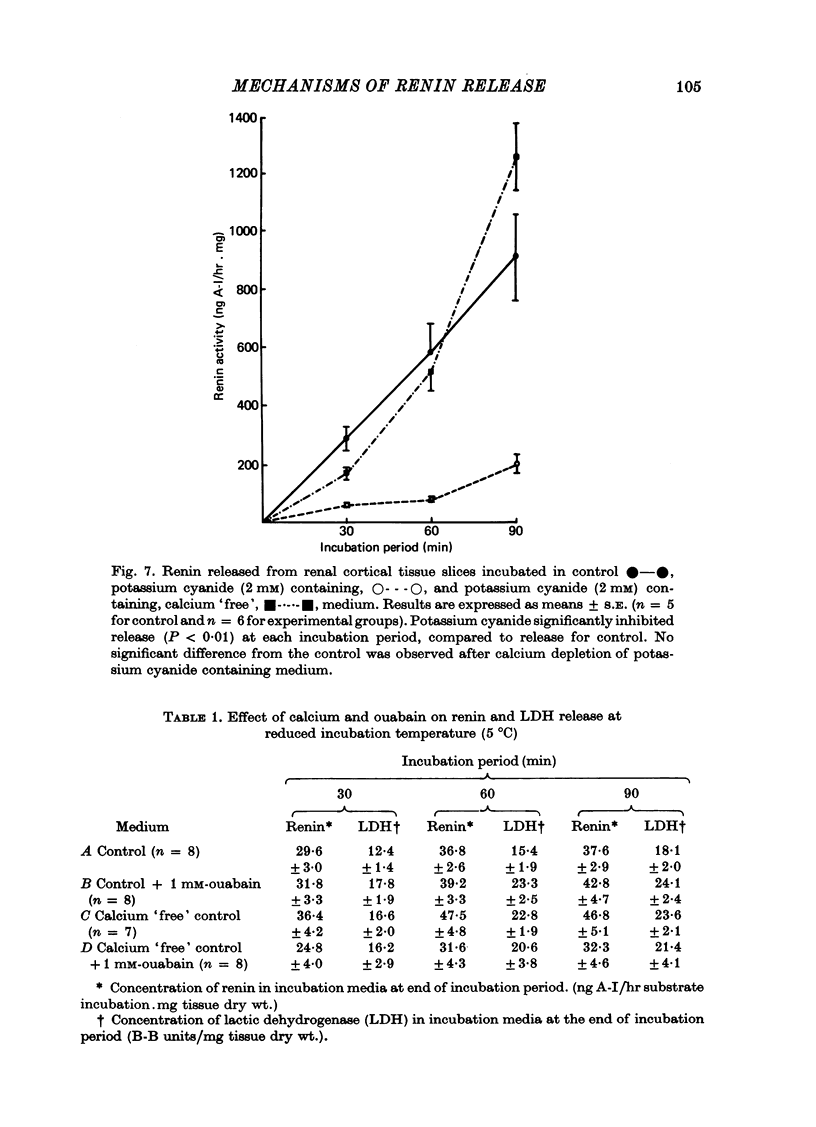
4. At reduced incubation temperatures (5 °C) the release of both renin and LDH were significantly reduced.
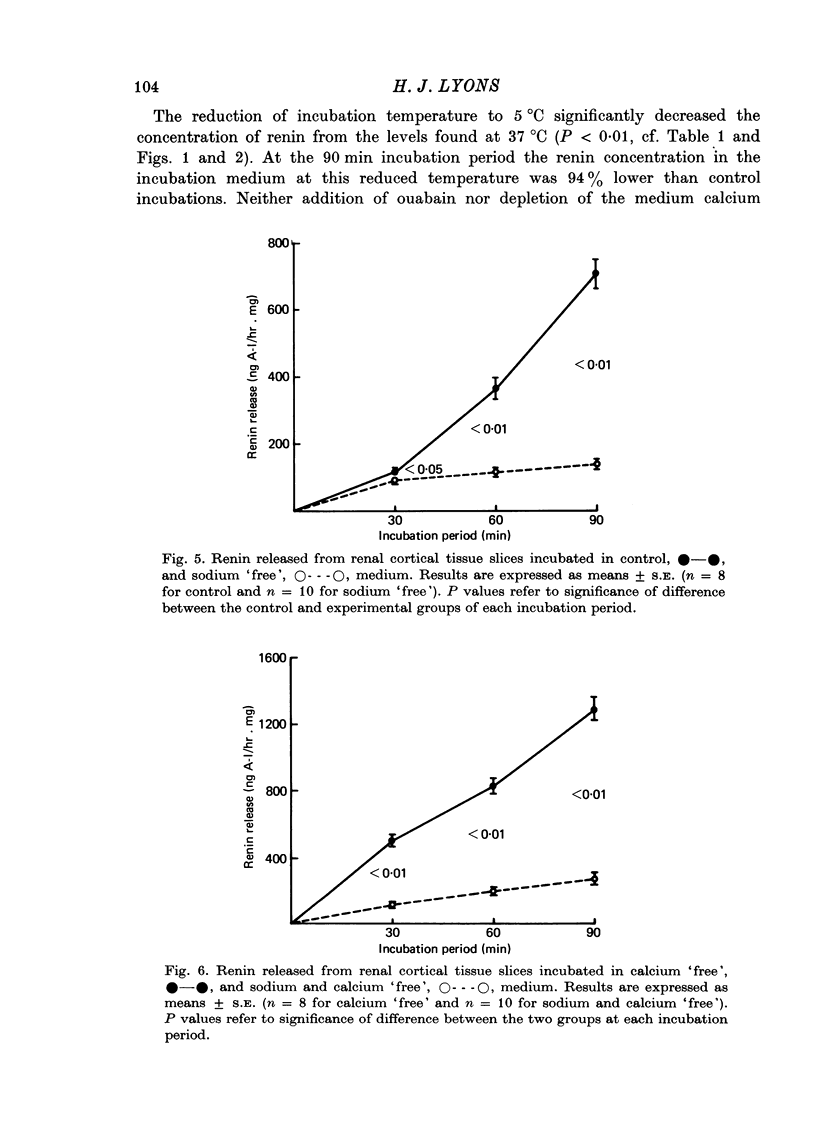
5. Medium sodium depletion caused a significant inhibition of renin release. The simultaneous removal of calcium from the medium did not restore renin release to control levels.
6. These results are not consistent with the hypothesis that spontaneous renin release during calcium depletion and metabolic inhibition is a result of cell enlargement and increased membrane permeability. On the other hand, the in vitro release of renin during these experiments appeared to be inversely related to the intracellular concentration of calcium.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks P. The effect of ouabain on the secretion of catecholamines and on the intracellular concentration of potassium. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):631–637. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach L., Leyssac P. P., Skinner S. L. Studies on renin release from isolated superfused glomeruli: effects of temperature, urea, ouabain and ethacrynic acid. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(1):243–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach L., Leyssac P. P. Studies on the mechanism of renin release from isolated superfused rat glomeruli: effects of calcium, calcium ionophore and lanthanum. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):745–764. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birks R. I., Cohen M. W. The influence of internal sodium on the behaviour of motor nerve endings. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jul 9;170(1021):401–421. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho J. S., Shapiro R., Hopper P., Page L. B. Methods for serial study of renin-angiotensin system in the unanesthetized rat. Am J Physiol. 1975 Feb;228(2):369–375. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.2.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. E., Williams J. A. Intracellular uptake and alpha-amylase and lactate dehydrogenase releasing actions of the divalent cation ionophore A23187 in dissociated pancreatic acinar cells. J Membr Biol. 1977 Apr 22;32(3-4):201–230. doi: 10.1007/BF01905220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. O., Freeman R. H. Mechanisms regulating renin release. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):1–56. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker S. E. Release of vasopressin and oxytocin from isolated pituitary glands of adult and new-born rats. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(2):429–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):451–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fynn M., Onomakpome N., Peart W. S. The effects of ionophores (A23187 and RO2-2985) on renin secretion and renal vasoconstriction. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):199–212. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M. Insulin and the pancreas. Vitam Horm. 1970;28:37–101. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60888-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada E., Lester G. E., Rubin R. P. Stimulation of renin secretion from the intact kidney and from isolated glomeruli by the calcium ionophore A23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 19;583(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester G. E., Rubin R. P. The role of calcium in renin secretion from the isolated perfused cat kidney. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(1):93–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons H. J., Chruchhill P. C. Renin secretion from rat renal cortical cell suspensions. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1835–1839. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons H. J., Churchill P. C. The influence of ouabain on in vitro renin secretion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Apr;145(4):1148–1150. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-37970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maude D. L. Effects of K and ouabain on fluid transport and cell Na in proximal tubule in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1969 May;216(5):1199–1206. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.5.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. S., Malvin R. L. Calcium in the control of renin release. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jul;235(1):F22–F25. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.1.F22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peart W. S., Quesada T., Tenyi I. The effects of EDTA and EGTA on renin secretion. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Feb;59(2):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert J., Brill W. A. Antagonism of experimental cyanide toxicity in relation to the in vivo acitivity of cytochrome oxidase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Aug;162(2):352–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Levi A. J. Cell damage and dye reduction in the quantitative nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) test. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Feb;19(2):309–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Control of renin release. Physiol Rev. 1967 Jul;47(3):359–382. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAM R., WILLIS J. S. ION MOVEMENTS AND OXYGEN CONSUMPTION IN KIDNEY CORTEX SLICES. J Physiol. 1963 Aug;168:158–177. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


