Abstract
1. The protein synthesis inhibitor, anisomycin, was given into the cerebral ventricles of rabbits as a priming dose followed by a continuous infusion. Doses of 100, 200 and 300 microgram followed by infusions at 100, 200 and 300 microgram/hr inhibited the incorporation of [14C] leucine into hypothalamic protein by over 90%. 2. Injection and infusion of anisomycin (300 microgram) suppressed the febrile response to leucocyte (endogenous) pyrogen given into the ventricles (I.C.V.) or I.V. 3. Dialysis experiments showed that anisomycin did not combine irreversibly with leucocyte pyrogen. 4. Anisomycin did not interfere with thermoregulation in a cold environment. 5. It is concluded that pyrogenesis may involve a step which is dependent on synthesis of hypothalamic protein with a rapid turnover.
Full text
PDF

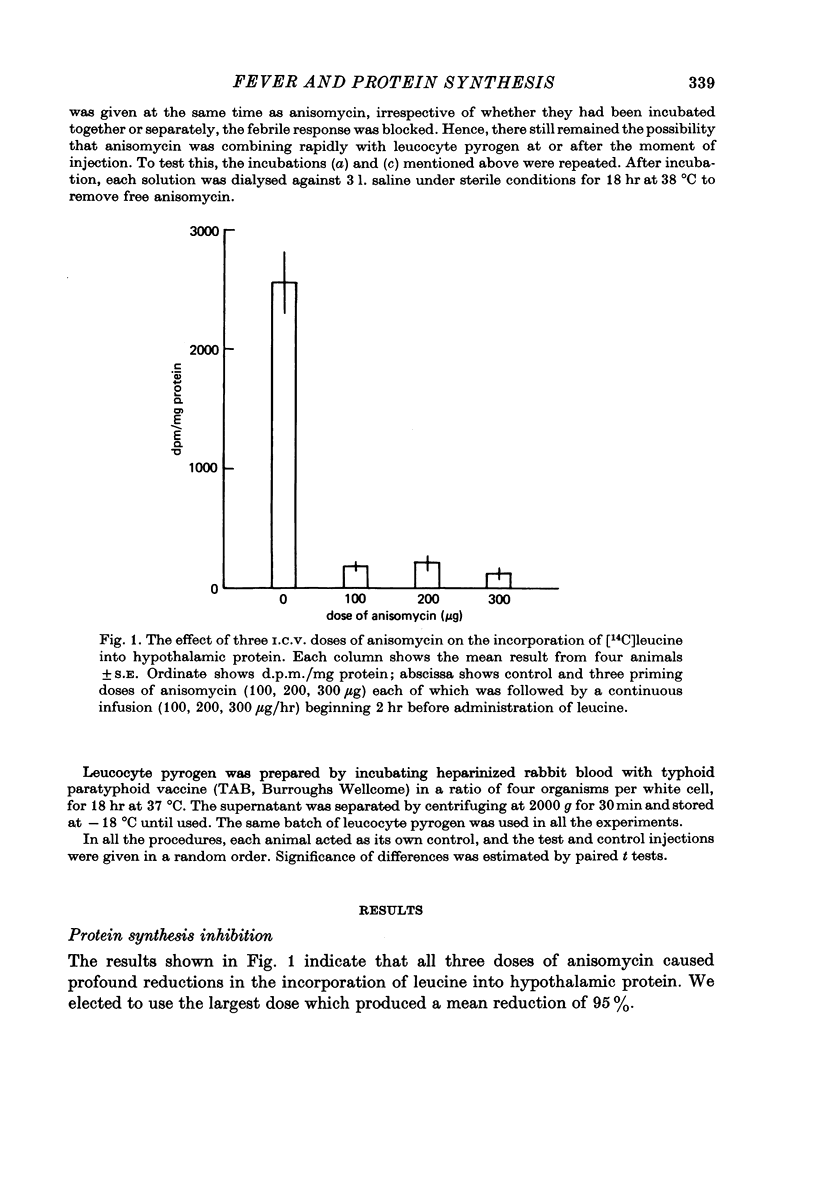
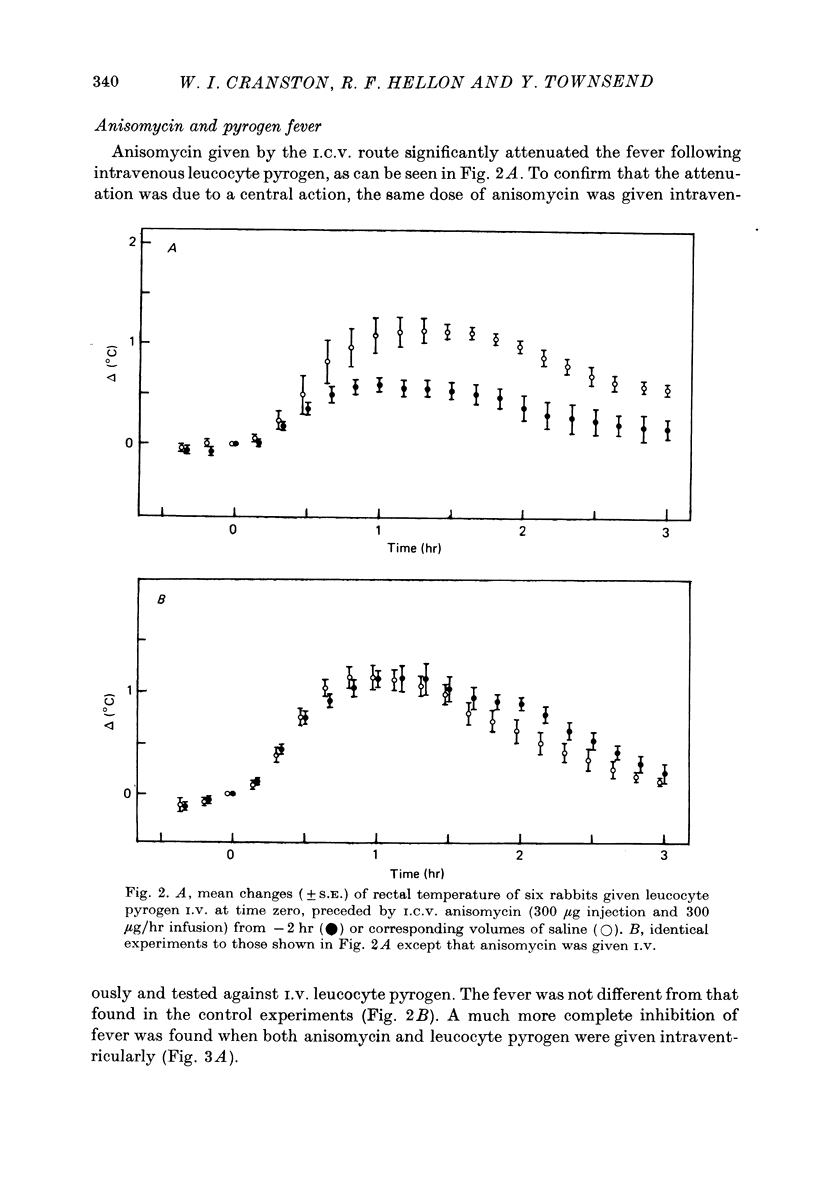
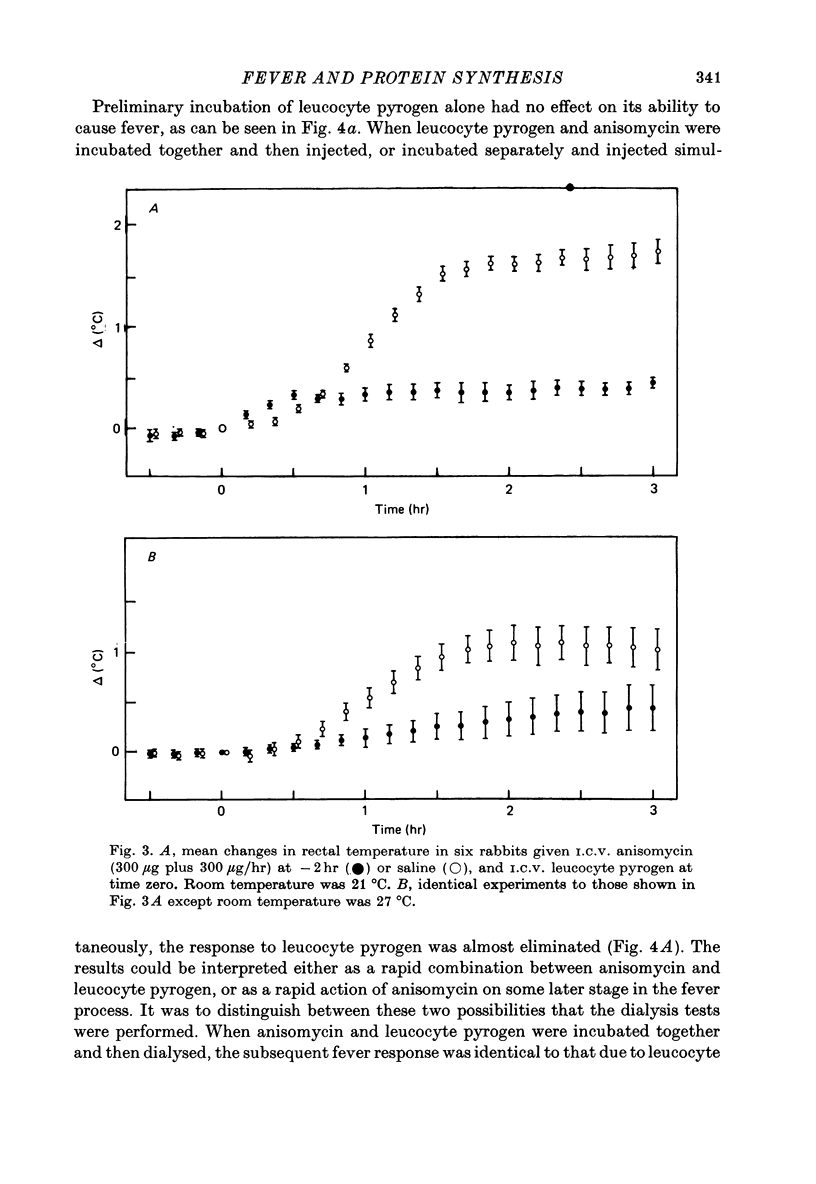
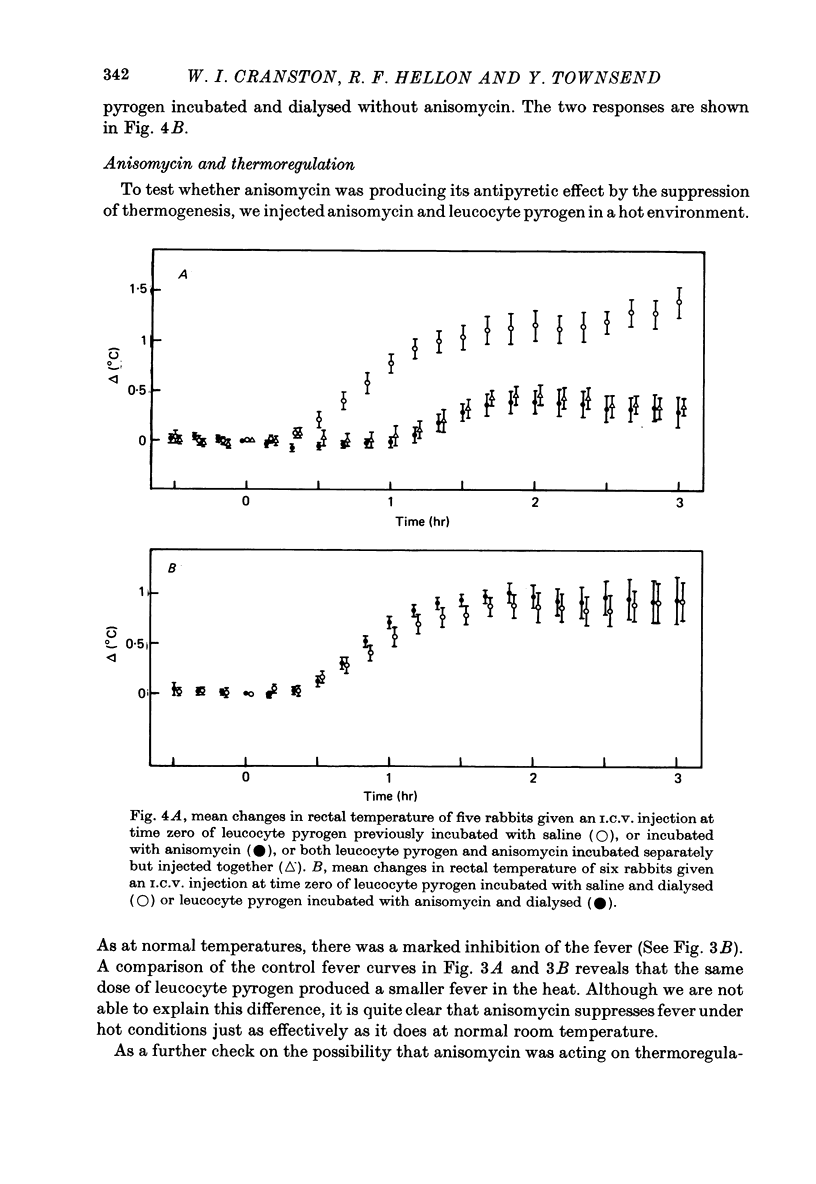

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barney C. C., Katovich M. J., Fregly M. J. Effect of cycloheximide on temperature regulation in rats. Brain Res Bull. 1979 May-Jun;4(3):355–358. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(79)80013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron I. R., Semple S. J. The central respiratory stimulant action of salicylates. Clin Sci. 1968 Oct;35(2):391–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranston W. I., Dawson N. J., Hellon R. F., Townsend Y. Contrasting actions of cycloheximide on fever caused by arachidonic acid and by pyrogen [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Dec;285:35P–35P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Production of endogenous pyrogen. Fed Proc. 1979 Jan;38(1):52–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame-Smith D. G. The prevention by inhibitors of brain proptein synthesis of the hyperactivity and hyperpyrexia produced in rats by monoamine oxidase inhibition and the administration of L-tryptophan or 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine. J Neurochem. 1972 Oct;19(10):2409–2422. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grollman A. P. Inhibitors of protein biosynthesis. II. Mode of action of anisomycin. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 10;242(13):3226–3233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegert R., Philipp-Dormston W. K., Radsak K., Menzel H. Mechanism of fever induction in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1130–1137. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1130-1137.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


