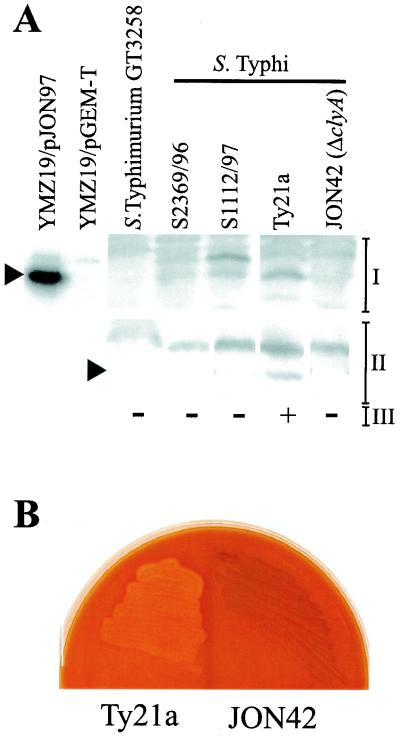
FIG. 5.
Phenotypic expression of ClyA cytotoxin by serovar Typhi Ty21a and loss of lytic phenotype upon inactivation of the clyASTy gene locus. (A) Western immunoblotting detection of ClyASTy protein content in serovar Typhi strains using a polyclonal ClyAEC antiserum (I) or a monoclonal antibody raised against ClyAEC (final dilution, 1:1,000) (II) and the ECL+ Western blotting detection system for visualization of immunoreactive bands (see Materials and Methods). The following approximate numbers of bacterial cells were used for the extracts loaded in the lanes. For the Salmonella strains, 3 × 108 cells were used for the polyclonal antiserum and 1 × 108 cells were used for the monoclonal antibody. For YMZ19/pJON97 (clyA::kan clyASTy+) and YMZ19/pGEM-T Easy (clyA::kan; vector), approximately 8 × 106 bacterial cells were used. The positions of reactive bands corresponding to ClyA are indicated with arrowheads on the left. The phenotypes of the strains on blood agar plates containing horse erythrocytes are indicated at the bottom (III) and were scored after 16 h of growth at 37°C (+, small lysis zones around individual colonies; −, no lysis). (B) Effect of inactivation of the clyASTy locus in serovar Typhi Ty21a. Shown are the phenotypes of Ty21a and the clyASTy in-frame deletion mutant JON42 on a blood agar plate containing horse erythrocytes after incubation at 37°C for 17 h.