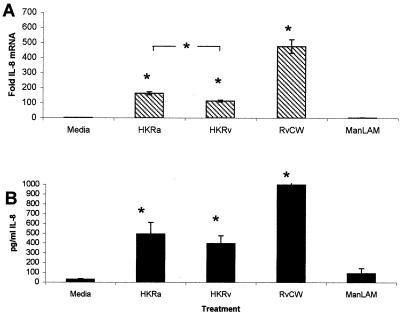
FIG. 4.
Ability of dead bacilli or their constituents to stimulate IL-8 production. (A) In vitro-cultured alveolar macrophages from BCG-vaccinated guinea pigs were stimulated with media alone, HKRa, HKRv, 10-μg/ml total cell wall harvested from H37Rv (RvCW), or 10-μg/ml ManLAM harvested from H37Rv (ManLAM) for 24 h. Total RNA from the macrophages was collected, reverse transcribed to cDNA, and detected by real-time PCR by using probes for IL-8 and 18s rRNA. Fold induction was determined from Ct values normalized for 18s expression and then normalized to the value derived from controls. Alveolar macrophages stimulated with heat-killed H37Ra, H37Rv, and total H37Rv cell wall showed significantly more IL-8 mRNA expression than did alveolar macrophages stimulated with media alone or H37Rv ManLAM. (B) Levels of guinea pig IL-8 protein were measured in the supernatants recovered from cultures of alveolar macrophage harvested from BCG-vaccinated guinea pigs stimulated with media alone, HKRa, HKRv, 10-μg/ml RvCW, or 10-μg/ml ManLAM harvested from H37Rv for 24 h by using the human IL-8 ELISA. Alveolar macrophages stimulated with HKRa, HKRv, and total H37Rv cell wall produced significantly more IL-8 protein than did alveolar macrophages stimulated with media alone or H37Rv ManLAM. All data are reported as means ± standard errors of the means. There were four animals per treatment group. Differences between groups were compared by Student's one-tailed t test, assuming equal variances. P values of <0.05 (*) were considered significant.