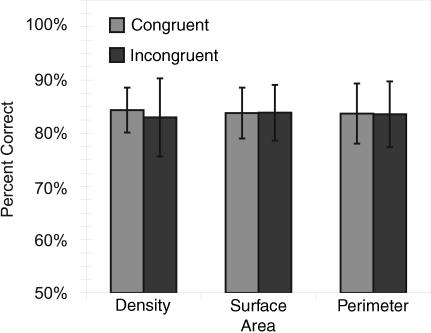
Fig. 2.
Accuracy when the number of dots in a stimulus was congruent (smaller number has smaller density, perimeter, or surface area) and incongruent (larger number has smaller density, perimeter, or surface area or when stimuli are equated on dimension) with density, cumulative surface area, and cumulative perimeter. Accuracy was not affected by these stimulus controls. The error bars reflect standard error between monkeys.