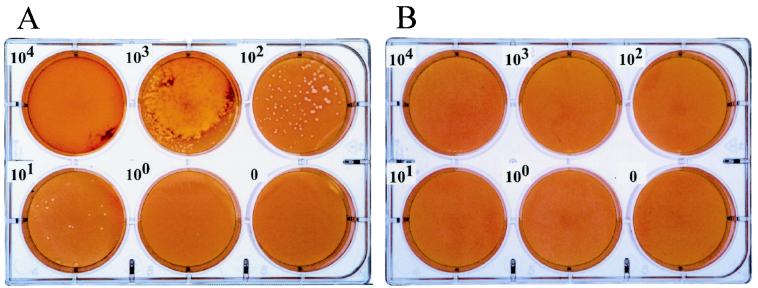
FIG. 1.
Comparative plaquing efficiency of C. trachomatis serovar D and C. pneumoniae strain AR-39 on murine McCoy cells. Chlamydiae were inoculated onto monolayers of McCoy cells at serial 10-fold dilutions ranging from 105 to 101 IFU per well and processed for plaque formation as described by Matsumoto et al. (12). C. trachomatis was incubated at 37°C, and C. pneumoniae was incubated at 35°C, for 10 days, respectively. The monolayers were then stained with neutral red to detect plaque formation. C. trachomatis formed distinct plaques in a dose-dependent manner by this assay, whereas no plaques were observed for C. pneumoniae strain AR-39 at any of the input IFU.