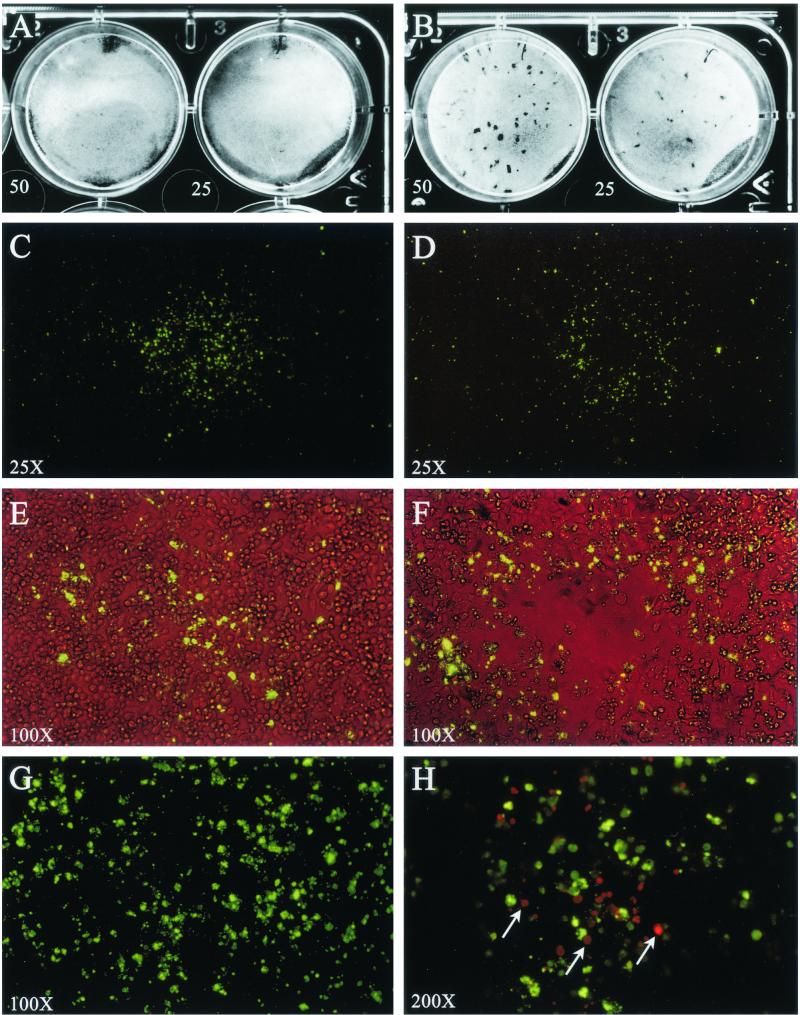
FIG. 2.
Focus and plaque morphology of C. pneumoniae AR-39 (A, C, E, G, and H) and TW-183 (B, D, and F) by immunostaining of viable HeLa 229 cell monolayers. Monolayers of HeLa 229 cells were infected with C. pneumoniae AR-39 or TW-183 at a multiplicity of infection of 50 and 25 IFU/well. After 10 days of incubation at 35°C, the infected monolayers were stained by IFA as either viable or fixed cells and examined for fluorescence. (A and B) Native monolayer after removal of the agarose overlay. AR-39 infection does not affect the monolayer (A), whileTW-183 forms small plaques with diameters of about 0.5 to 1.5 mm (B). (C and D) Monolayer of viable cells incubated with anti-MOMP MAb GZD1E8 followed by staining with FITC-labeled goat anti-mouse antibody (total magnification, ×25). Note positive-staining focus on the monolayer's surface exhibiting a galaxy-like fluorescence pattern. The staining of the foci is noncontiguous and radiates in a circumferential pattern away from its center. Foci ranged in size from 0.5 to 3.0 mm. (C) The focus shown (strain AR-39) is approximately 1.8 mm in diameter. (D) Some foci of TW-183 show a central clearing in the fluorescence pattern. (E and F) Similar foci to those shown in panels C and D but observed by simultaneous phase and fluorescent microscopy (magnification, ×100). While AR-39 does not affect the confluency of the monolayer (E), most foci of TW-183 show a central cell lysis (F) that is correlated to the central clearing of fluorescence shown in panel D. (G) Same focus as that shown in panel C but viewed at a magnification of ×200. The immunostaining with MOMP MAb produced a nonstructural nonuniform punctate staining pattern on the surface of the monolayer. (H) A monolayer stained for foci (AR-39), fixed with methanol, and secondarily stained with anti-MOMP and a TRITC-labeled goat anti-mouse antibody (magnification, ×200). C. pneumoniae inclusions (red) were found in HeLa cells underlying the infection focus (green). Inclusions were only observed in association with foci, demonstrating that the source of antigen detected on the viable cell surface was derived from the underlying infected cells of the monolayer.