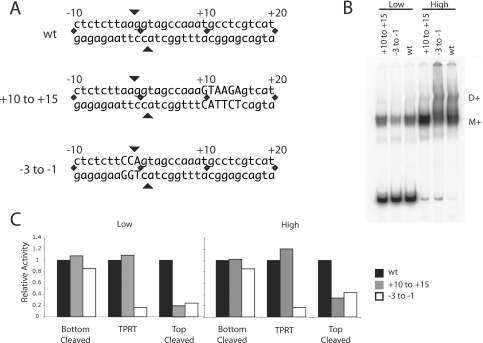
Figure 4.
Mutation of the target DNA at the ZF and Myb-binding sites. (A) DNA substrates used in the binding, cleavage and TPRT reactions. The DNA substrate extended from 70 bp upstream to 30 bp downstream but only the sequences near the R2 insertion site are shown. Mutations of the +10 to +15 region (Myb-binding site) and −3 to −1 (ZF-binding region) are indicated by capital letters. All mutations involved G–T and A–C transversions. (B) Gel shifts of the full-length R2 protein bound to mutant DNA substrates at low (36 fmol) and high (360 fmol) protein concentrations in the absence of dNTPs. Eighty fmol of the DNA substrate and 430 fmol of R2 RNA were present in each binding assay. M+, protein monomer with RNA; D+, protein dimer plus RNA. (C) DNA cleavage and TPRT activity of the R2 protein on the wild-type (WT), +10 to +15 mutant and −3 to −1 mutant DNA substrates. The incubation conditions were identical to that in (B). After the incubation the fraction of DNA cleaved was determined on denaturing polyacrylamide gels, while EMSA gels were used to the calculate the fraction of DNA bound. Cleavage reactions were conducted in both the presence and absence of dNTPs and the results averaged. Activity is reported as per bound unit of DNA with the activity observed on the WT DNA substrate set at 100% (black bar). Gray bars, data for the +10 to +15 mutant DNA substrate; white bars, data for the −3 to −1 DNA substrate.