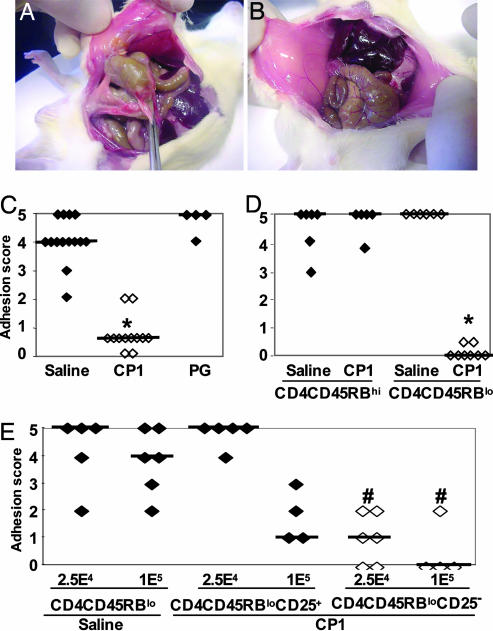
Fig. 1.
T cells mediated protection against surgical adhesion by ZPS. (A) Male C57BL/6 mice were injected s.c. with saline or CP1 (50 μg per mouse) -24, 0, and +24 h relative to cecal abrasion surgery. Six days later, animals were examined and scored for the severity of adhesions as described in Materials and Methods. Saline-treated animals exhibited dense vascularized adhesions involving the cecum and opposing abdominal wall. (B) CP1-treated mice exhibited fewer and less severe adhesions. (C) Mice were treated as above with saline (filled symbols), CP1 (open symbols), or PG (filled symbols) and subjected to cecal abrasion. Animals treated with CP1 had significantly lower adhesion scores than saline- or PG-treated animals (*, P < 0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test). (D) CD4+CD45RBlo T cells from CP1-treated mice transfer protection against adhesion formation. Groups of mice were treated with saline or CP1 (50 μg per mouse) on three successive days, and splenic CD4+ T cells were isolated 1 day after the final treatment. Cells were stained with CD45RB-specific Ab and high- and low-expressing populations isolated by FACS. A total of 5 × 104 cells of each population were then transferred i.c., and animals were subjected to cecal abrasion 24 h later. Animals receiving CD4+CD45RBhi T cells (filled symbols) from saline or CP1-treated animals developed severe adhesions. Mice receiving CD4+CD45RBlo T cells (open symbols) from saline-treated mice developed severe adhesions, whereas mice receiving CD4+CD45RBlo T cells from animals treated with CP1 had significantly lower adhesion scores (*, P < 0.001 compared with CD4+CD45RBlo T cells from saline-treated mice). (E) CP1 protective effect is preferentially transferred by CD4+CD45RBloCD25- T cells. Groups of mice were treated with saline or CP1 on three successive days as described above. Splenic CD4+ T cells were isolated and double-stained with CD45RB- and CD25-specific antibodies, and CD4+CD45RBloCD25+ and CD4+CD45RBloCD25- were purified by FACS. A total of 2.5 × 104 or 1 × 105 cells of each population were then transferred i.c. to animals subjected to cecal abrasion 24 h later. Mice receiving 2.5 × 104 CD4+CD45RBloCD25+ T cells from animals treated with CP1 developed severe adhesions, whereas mice receiving more (1 × 105) such cells had lower adhesion scores but were not significantly different from animals given CD4+CD45RBlo T cells from saline-treated mice. Animals receiving 2.5 × 104 or 1 × 105CD4+CD45RBloCD25- T cells (open symbols) had significantly lower adhesion scores compared with CD4+CD45RBlo T cells from saline-treated mice (#, P < 0.005). All animal experiments were performed at least two times, and the results were combined.