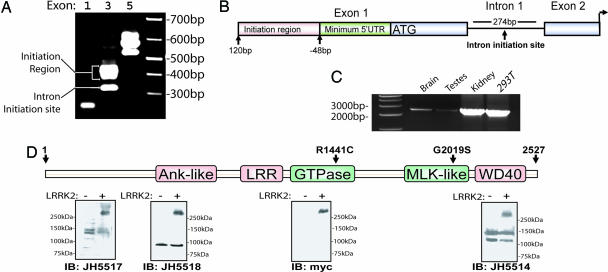
Fig. 1.
Characterization of expression of LRRK2. (A) 5′-RACE nested PCR using human total brain cDNA, as resolved on an ethidium bromide agarose gel. The exon position of the corresponding reverse oligonucleotide in the predicted LRRK2 transcript is given. (B) Diagram depicting the 5′ end of the LRRK2 gene. The ATG represents the presence of the first consensus Kozak sequence downstream of the initiation region and the start of the predominant LRRK2 ORF. (C) RT-PCR using oligonucleotide primers spanning the 3′ end of the predicted LRRK2 transcript. Sources of cDNA derived from human tissue or cell lines are indicated. (D) Protein domain structure of LRRK2 where the ankryin (Ank-like) repeat region, the leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain, the GTPase domain, the MLK-like domain, and the WD40 domain positions are indicated. Lysate derived from HEK-293T cells transiently expressing myc-tagged LRRK2 (+) or empty (-) vector were analyzed by Western blotting by using LRRK2-specific antibodies with recognition sites near the N terminus (JH5517 and JH5518) or the C terminus (JH5514 and anti-myc).