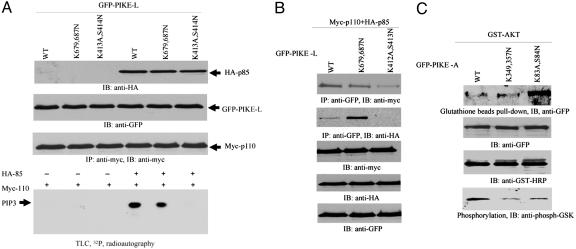
Fig. 4.
PH domain of PIKE mediates its activation of PI3-kinase and Akt. (A) PI3-kinase assay in PIKE-L-transfected HEK293 cells. GFP-PIKE-L WT, (K679,687N), and (K413A,S414N) constructs were transfected into HEK293 cells with myc-p110 and HA-p85, respectively. PI3-kinase was pulled down with anti-myc Ab. PI3-kinase assay was performed in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. In the absence of HA-p85, no PI3-kinase activity is observed. WT PIKE-L strongly provokes PI3-kinase activity. In contrast, PIKE-L(K413A,S414N) completely inhibits it. Strikingly, K679,687N mutation decreases PI3-kinase activity (bottom image). The expression of all transfected constructs is verified (first, second, and third images from top). (B) PIKE-L binds PI3-kinase. GFP-PIKE-L WT, K679,687N, and K413A,S414N constructs were transfected into 293 cells with myc-p110 and HA-p85, respectively. PIKE-L was immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP Ab. The beads-associated proteins were analyzed with anti-HA or anti-Myc Ab. All PIKE-L constructs interact with the catalytic subunit p110. However, PIKE-L (K413A,S414N) mutant does not bind to the regulatory subunit p85. Interestingly, K679,687N mutant binds to more p85 than WT PIKE-L (first and second images from top). (C) PIKE-A binds to Akt. GST-Akt was transfected into HEK293 cells with PIKE-A WT, (K349,357N), and (K83A,S84N) mutants, respectively. Akt was pulled down with glutathione beads, and the associated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting assay with anti-GFP Ab. In the absence of EGF, PIKE-A (K83A,S84N) more potently binds to Akt than WT PIKE-A does. PIKE-A (K349,357N) reveals the comparable binding affinity to Akt as WT (top image). The expression of transfected constructs is verified (second and third images from top). In vitro Akt kinase assay with GSK3 demonstrates that WT presents highest activity than other two mutants (bottom image).