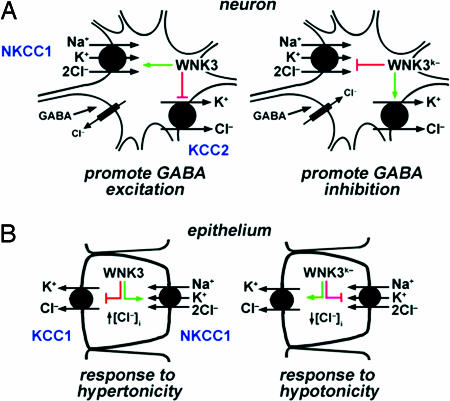
Fig. 5.
Proposed physiologic roles of WNK3. (A) WNK3 regulation of the neuronal response to GABA. Kinase-active WNK3 can increase [Cl-]i by increasing activity of NKCC1 and inhibiting KCC2, promoting an excitatory response to GABA. Kinase-dead WNK3 inhibits NKCC1 and activates KCC2, potentially promoting neruonal inhibition. (B) WNK3 regulation of cell volume. WNK3 can increase [Cl-]i by activating NKCC1 and inhibiting KCC1; kinase-inactive WNK3 could decrease [Cl-]i by inhibiting NKCC1 and activating KCC1. These are activities required to maintain cell volume in response to hyper- and hypoosmolar stress, respectively.