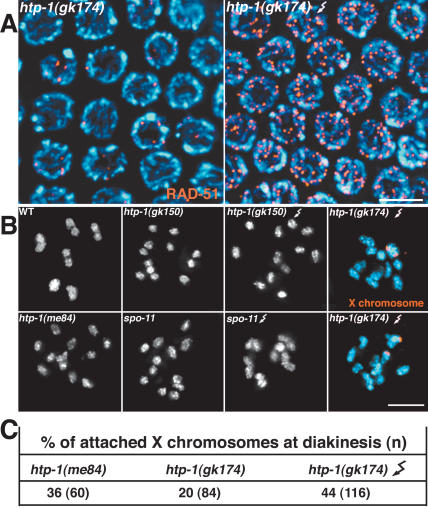
Figure 8.
γ-Irradiation of htp-1 mutants does not fully rescue chiasma formation between the X chromosomes. (A) α-RAD-51 immunostaining of mid-pachytene region nuclei from an untreated htp-1 mutant worm (left) and an htp-1 worm treated with 5000 rads of γ-irradiation and fixed 1 h later (right). (B) Each panel shows the DAPI-stained chromosomes (white or blue) from a single diakinesis-stage oocyte nucleus of the indicated genotype. Crooked arrows indicate nuclei from worms that had been exposed to 5000 rads of γ-irradiation and then fixed and stained 18 h later. Orange in the right panels corresponds to FISH signals used to identify the X chromosomes. Wild-type (WT) nuclei show six bivalents, while htp-1 and spo-11 mutants typically show 12 unattached chromosomes (univalents). Following γ-irradiation, chiasma formation is efficiently restored in spo-11 mutants (six bivalents present) but not in htp-1 mutants. Bars, 5 μm. (C) The table shows quantitation of diakinesis nuclei showing chiasmata between the X chromosomes in htp-1 mutants.