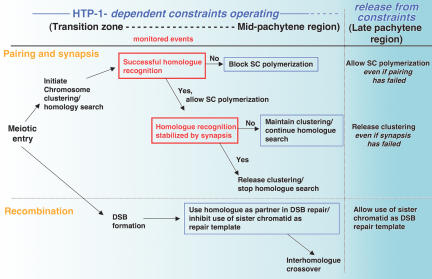
Figure 9.
Model in which HTP-1-dependent constraints govern key aspects of the meiotic program. We propose that HTP-1 functions to establish or maintain constraints that operate during early prophase to (1) couple SC polymerization with successful homolog recognition, (2) couple release from chromosome clustering and termination of homology search with stabilization of pairing through synapsis, and (3) inhibit the use of sister chromatids as recombination partners. Whereas during wild-type meiosis the conditions for proceeding with synapsis and chromosome dispersal are usually met early within the domain in which the proposed constraints operate, analysis of mutants provides evidence for continued operation of these constraints through the mid-pachytene region of the gonad. We further propose that these constraints are lifted in the late-pachytene region of the gonad. Red boxes indicate monitored events; blue boxes indicate functions that require HTP-1. See text for further discussion.