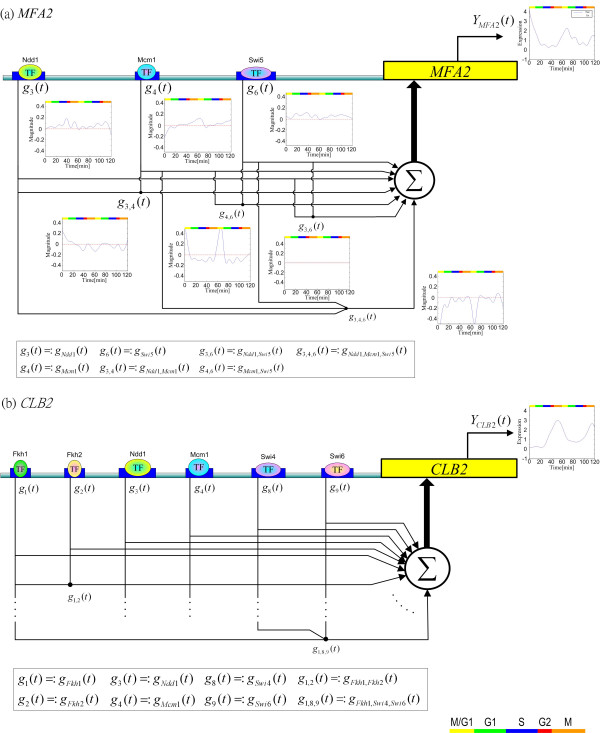
Figure 1.
Dynamic model of the cis-regulatory circuit of gene MFA2 (a) and of gene CLB2 (b). The genome-wide TF-binding location data obtained using chromatin immunoprecipitation [4] is used to identify the transcription factor binding motifs (cis elements). A binding transcription factor p has a regulatory function gp(t) and interacts with other recognizing TFs to produce the regulatory functions gp,q(t) and gp,q,r(t). These regulatory functions are the inputs of the cis-regulatory circuit and generate the dynamic output (i.e., the expression profile) of the target gene. Different phases of the cell cycle are indicated by the colored bar at the right lower corner.