Figure 1.
Genomewide linkage results for asthma and related traits. Autosomes are arranged by number from p-ter to q-ter, with genetic distance expressed as Kosambi cM (0–3,548 cM). A–D, For the four affection traits, the Whittemore and Halpern (1994) Sall statistic was calculated, and Z scores were converted into LOD scores by use of the Kong and Cox (1997) exponential model implemented in MERLIN 1.0. LOD scores were then converted to empirical pointwise −log10P values by use of 1,000 genome-scan replicates simulated under the null hypothesis of no linkage. The same replicates were used to estimate the thresholds for genomewide suggestive and significant linkage (see main text). The number of families with two or more affected sibs was 34 for asthma, 49 for BHR, 115 for atopy, and 69 for Dpter. E–G, For the three continuous traits, IBD probabilities were imported into SOLAR, and maximum-likelihood univariate variance-components linkage analysis was performed with the fixed effects of covariates (see main text) and proband-ascertainment correction. LOD scores were converted to empirical pointwise −log10P values, and genomewide thresholds were estimated as described above. The minimum value for the Y-axis corresponds to −log10(.5) (i.e., LOD=0). The top horizontal line shows the empirical genomewide threshold for significant linkage (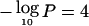 , for all traits), and the bottom line, for suggestive linkage (
, for all traits), and the bottom line, for suggestive linkage (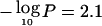 ). H, Multipoint entropy information content (Kruglyak et al. 1996). The average information content was 0.57, computed with MERLIN at the marker closest to the middle of the chromosome and averaged over the 22 autosomes.
). H, Multipoint entropy information content (Kruglyak et al. 1996). The average information content was 0.57, computed with MERLIN at the marker closest to the middle of the chromosome and averaged over the 22 autosomes.

