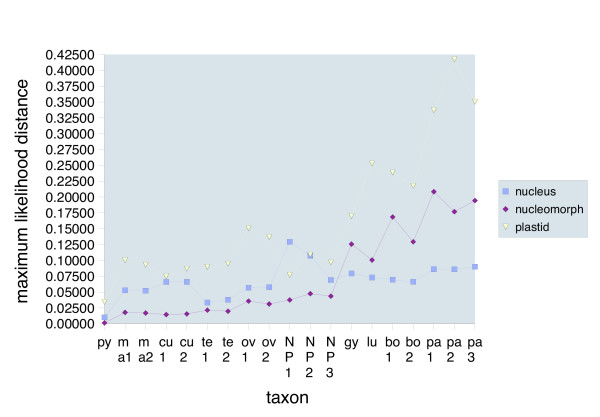
Figure 2.
Chart diagram displaying genetic divergences among the taxa and across the three data sets. A strain from a clade with inconspicuous branch lengths in all three phylogenies, Cryptomonas pyrenoidifera strain M1077, was chosen as a reference. The distance values represent the genetic divergences of strain M1077 to the other taxa. The distance values were extracted from the maximum likelihood distance matrices used otherwise by Paup to infer the neighbor-joining trees during phylogenetic analyses, and fed into a spread-sheet program. Strains CCMP 152, CCAC 0031 and M2180 were genetically identical to strains M1077, CCAP 979/46 and CCAC 0056, respectively, thus, were omitted from the chart diagram. Nucleus, concatenated nuclear SSU rDNA, ITS2 and partial LSU rDNA; nucleomorph, nucleomorph SSU rDNA; plastid, rbcL gene. Taxon designations (abscissa): py, C. pyrenoidifera CCAP 979/61; ma1, C. marssonii CCAC 0086; ma2, C. marssonii CCAC 0103; cu1, C. curvata CCAC 0006; cu2, C. curvata CCAC 0080; te1, C. tetrapyrenoidosa M1092; te2, C. tetrapyrenoidosa NIES 279; ov1, C. ovata CCAC 0064; ov2, C. ovata M1171; NP1, NoPyr strain CCAP 979/46; NP2, NoPyr strain CCAC 0109; NP3, NoPyr strain M0741; gy, C. gyropyrenoidosa CCAC 0108; lu, C. lundii CCAC 0107; bo1, C. borealis CCAC 0113; bo2, C. borealis SCCAP K-0063; pa1, C. paramaecium M2452; pa2, C. paramaecium CCAP 977/1; pa3, C. paramaecium CCAC 0056.