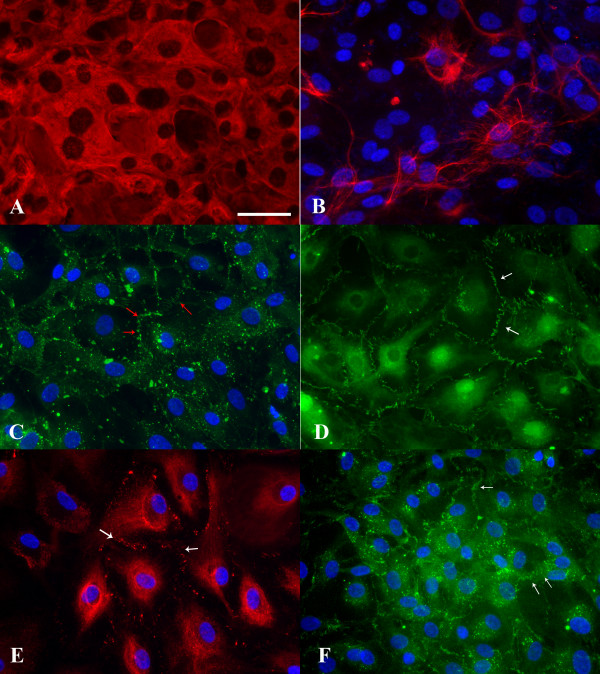
Figure 2.
Immunocytochemical staining of confluent cell cultures from human AG tissue on fibronectin coverslips. A: Arachnoidal cells in culture were incubated with a Cy3 conjugated anti-vimentin antibody. Cells expressed this intermediate filament protein uniformly throughout the cytoplasm. B: Arachnoidal cells were labeled with a broad spectrum anti-cytokeratin antibody and visualized with a FITC conjugated secondary antibody. Cells expressed the epithelial specific intermediate filament protein cytokeratin in a perinuclear pattern, though the expression of this protein was not uniform. C: Cells cultured from AG tissue were incubated with a connexin43 antibody and then visualized with a FITC conjugated secondary antibody. Immunolocalization of this protein in a punctuate pattern at cell-cell borders (red arrows) indicates that arachnoidal cells are able to form gap junctions in confluent culture. D: Tight junctions in confluent cultures were identified by immunoreactivity to a FITC conjugated ZO-1 antibody. The antibody deposition pattern can be seen at cell-cell borders (white arrow) with overlapping filapodia consisting of short linear structures in parallel. E: Arachnoidal cells in culture were labeled with an anti-desmoplakin antibody and revealed with an Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated secondary antibody. Confluent cultures were able to form desmosomes as evidenced by the punctuate staining along the membranes of adjacent cell borders (white arrows). F: E-cadherin immunoreactivity was demonstrated by incubating cells with a FITC conjugated antibody to E-cadherin. This epithelial specific cell adhesion molecule was expressed at the periphery of the cells, at cell-cell contacts (white arrows) in a pattern similar to that of connexin43 or ZO-1. All immunofluorescent images were taken at the same magnification. Bar= 50 μm.