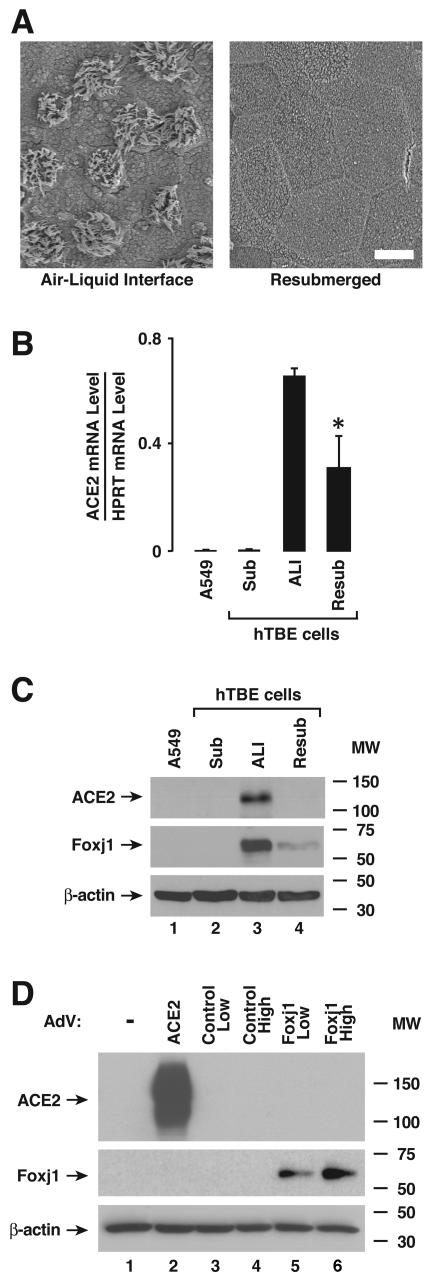
FIG. 2.
ACE2 expression is associated with airway epithelial cell differentiation. (A) Ciliated epithelial cell differentiation in cultures of primary airway epithelial cells under air-liquid interface or resubmerged conditions was verified by SEM of the apical epithelial surface. Bar, 10 μm. (B) ACE2 mRNA levels were determined using real-time RT-PCR analysis of samples from A549 cells or primary hTBE cells cultured under undifferentiating submerged (Sub), differentiating ALI, or resubmerged (Resub) conditions. Values are expressed as mean mRNA levels relative to control HPRT mRNA levels plus or minus standard deviations (SD) (n = 3), and the asterisk indicates a significant difference in mRNA levels between air-liquid interface and resubmerged conditions. (C) ACE2 protein levels were determined using immunoblot analysis of extracts from A549 or primary hTBE cells. The positions of ACE2, foxj1 (to verify epithelial cell differentiation status), and β-actin are indicated by arrows. MW, molecular weight in thousands. (D) ACE2 protein levels were determined using immunoblot analysis of extracts from hTBE cells under submerged conditions that were infected with a recombinant adenoviral vector that expressed ACE2, control transgene (β-galactosidase), or foxj1. MW, molecular weight in thousands.