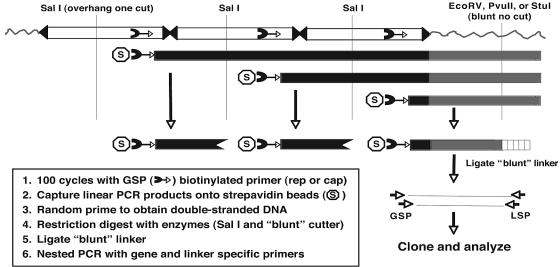
FIG. 2.
Schematic of linear amplification mediated PCR (LAM-PCR) to detect random AAV integrants. To isolate DNA sequences flanking integrated wild-type AAV genomes, linear PCR (100 cycles) was performed on total cellular DNA (1 μg) using an AAV-specific biotinylated primer homologous to a conserved region in the cap or rep gene (cap is shown). PCR products were captured on streptavidin beads and converted to double-stranded DNA by random hexanucleotide priming. The double-stranded DNA was then digested with a blunt-cutting restriction enzyme (EcoRV, PvuII, or StuI) to generate a substrate for ligation of a blunt linker (vertical box) to the end of the digested DNA. To reduce the level of competing internal AAV-AAV junctions, double stranded fragments were also digested with SalI, which created an incompatible end for ligation of the blunt adaptor. The resulting DNA fragments were subjected to two rounds of PCR using AAV and linker-specific primers. PCR products were analyzed by Southern hybridization and cloned into an appropriate PCR vector for subsequent analysis.