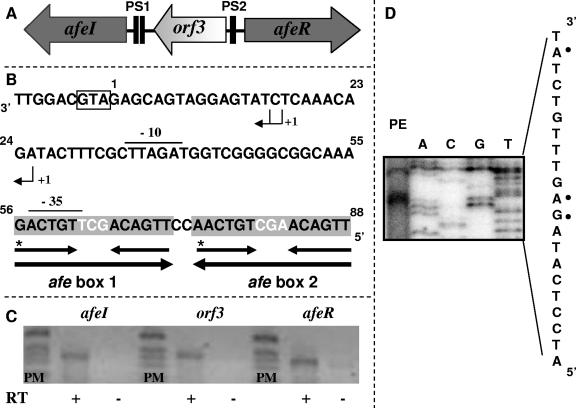
FIG. 4.
Quorum-sensing genetic locus of A. ferrooxidans. (A) Schematic map of the quorum-sensing locus of A. ferrooxidans composed of three genes: afeR encoding the transcriptional regulator, afeI encoding the AHLs synthase, and orf3 having an unknown function. Two palindromic sequences (PS1 and PS2) were located (solid boxes). (B) Nucleotide sequence of the putative afe boxes. The large palindromic sequence (PS1) was conformed by a 32-bp palindromic sequence (large arrows) which was built over internal, hierarchical and smaller palindromic sequences (small arrows) called afe box 1 and afe box 2. The box at the 3′ end indicates the translational start codon for afeI. +1 indicates the transcriptional initiation sites identified; overlining indicates the E. coli σ70-type promoter; and asterisks indicate the purine base transition at the 3′ ends of the afe boxes. (C) Transcription analysis of the quorum-sensing genetic locus by RT-PCR analysis. RT reactions were carried out with 1 μg of total RNA from thiosulfate-grown A. ferrooxidans cells and were performed with (+) and without (−) the Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase in order to exclude amplification due to genomic DNA contamination. RT-PCR products were analyzed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. (D) Determination of transcriptional initiation sites for the afeI gene by a primer extension experiment. The relevant DNA sequence (complementary to the sequence shown in panel B between nucleotides 8 and 27) is shown on the right, and the positions of the possible start sites are indicated by solid dots.