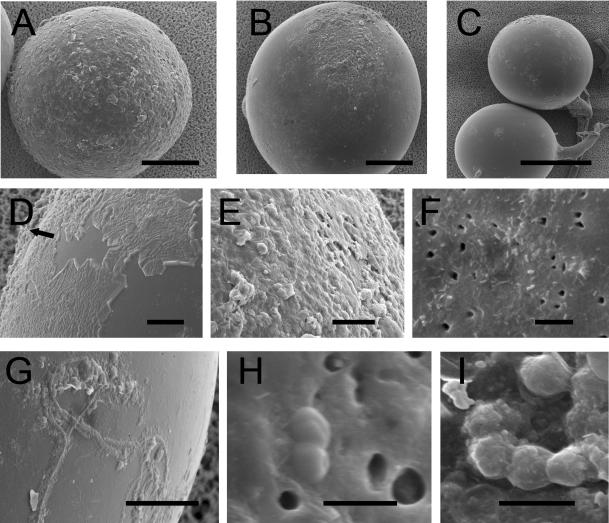
FIG. 5.
SEM images of the surface of G. geosporum spores. (A) Young, light yellow-brown spore with its sloughed and eroded outer hyaline layer covering the whole surface; (B) older, medium-brown spore with a residual outer hyaline layer; (C) old, dark orange-brown spore that has lost almost all its outer hyaline layer; (D) outer hyaline layer starting to “peel off” and being replaced by mucilaginous products (arrow); (E) mucilaginous outer hyaline layer; (F) bacterial cells of various shapes adhering to the surface of the laminated layer, with holes possibly corresponding to lysis zones in the spore wall; (G) filamentous bacterial cells adhering to the laminated layer covered with mucilaginous products; (H) coccus-shaped bacteria in division state on the spore surface; (I) chain of coccus-shaped bacteria covered with mucilaginous products. Bars (in micrometers): A and B, 50; C, 100; D, E, F, and G, 10; H and I, 1.