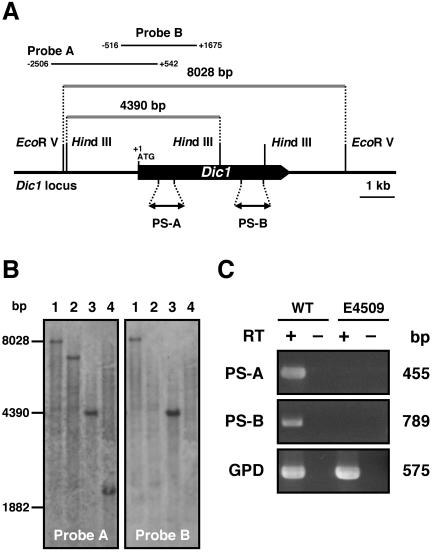
FIG. 1.
dic1 deficiency in strain E4509 of C. heterostrophus. (A) Schematic representation of the chromosomal DIC1 locus in the wild-type strain HITO7711. The restriction enzyme sites, the point at which the probes hybridize, and the site amplified by RT-PCR are indicated. (B) Southern analysis of the dic1 locus in the wild-type and dic1 mutant strains. Chromosomal DNA of the wild-type strain HITO7711 (lanes 1 and 3) and of the dic1 mutant strain E4509 (lanes 2 and 4) was digested with EcoRV (lanes 1 and 2) or HindIII (lanes 3 and 4). An approximately 3-kb DNA fragment was first used as the probe (probe A), and, after reprobing, an approximately 2-kb DNA fragment (probe B) was hybridized. (C) Dic1 gene expression in the wild-type and dic1-deficient strains. RNA isolated from the wild-type strain HITO7711 (WT) and the dic1-deficient strain E4509 was used for cDNA synthesis. The cDNA synthesized (+) or not synthesized (−) with reverse transcriptase was used as the template for RT-PCR. The RT-PCR products amplified by two specific primer sets (PS-A and PS-B) and the primers for the C. heterostrophus GPD gene, a positive control, were separated by electrophoresis.