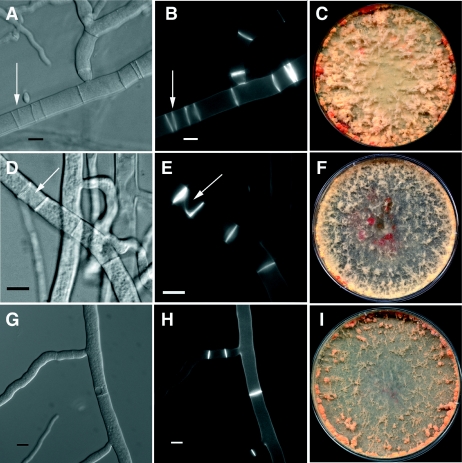
FIG. 6.
Phenotype of strains containing active alleles of rho-4 in N. crassa. (A) Differential interference contrast (DIC) image of CR28-1 (his-3+::Pgpd-HA-Q69L-rho-4; rho-4) showing multiple, closely positioned septa. An arrow points to an irregular septum. (B) Calcofluor-stained fluorescent image of the same hypha as in panel A. (C) Petri dish showing the phenotype of CR28-1 containing the Q69L rho-4 allele. The bright orange dots at the periphery of the plate are due to cytoplasmic bleeding. (D) DIC image of CR29-1 (his3+::Pgpd-HA-G18V-rho-4; rho-4). The arrow points to an incorrectly formed septum. (E) Calcofluor-stained fluorescent image of the same hypha as in panel D. Same arrow as in panel D. (F) Petri dish showing the cytoplasmic bleeding phenotype of CR29-1 (G18V rho-4 allele). (G) DIC image of CR31-1 (his3+::Pgpd-HA-D126A-rho-4; rho-4). (H) Calcofluor-stained hyphae of same hyphae as in panel G. This strain does not show numerous multiple, incorrectly positioned septa as found in CR28-1 or CR29-1, although septation is highly irregular. (I) Petri dish showing the clumpy conidiation phenotype of CR31-1 (D126A rho-4 allele). Bar, 10 μm.