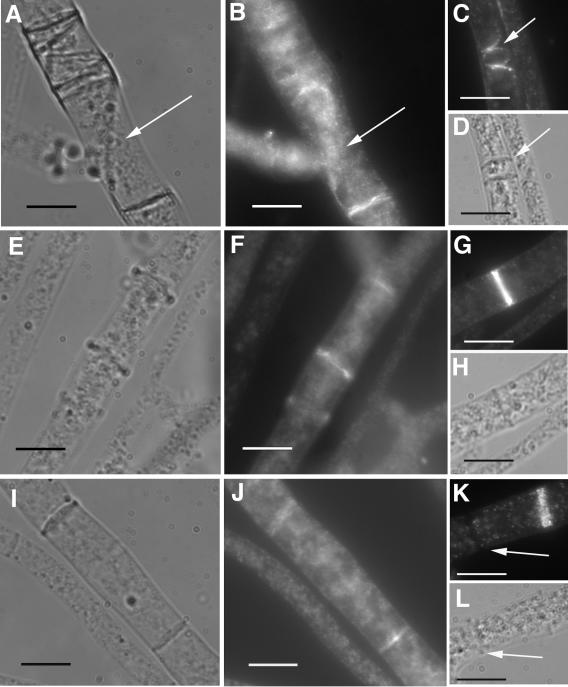
FIG. 7.
Immunolocalization of epitope-tagged activated RHO-4 proteins using anti-HA antibodies. (A) Differential interference contrast (DIC) and (B) fluorescence images of CR28-1 (his3+::Pgpd-HA-Q69L-rho-4; rho-4−) show localization of HA-Q69L-RHO-4 to incorrectly positioned septa (arrow). (C) Actin localization in CR28-1. An arrow points to aberrant actin rings which presumably will lead to aberrant septa. (D) DIC image of panel C showing septa. (E) DIC and (F) fluorescence images of CR29-1 (his3+::Pgpd-HA-G18V-rho-4; rho-4−) show a localization pattern of HA-G18V-RHO-4 at septa that is similar to that of wild-type strains. (G) Actin localization in CR29-1 showing a normal actin ring. (H) DIC image of panel G. (I) DIC and (J) fluorescence images of CR31-1 (his3+::Pgpd-HA-D126A-rho-4; rho-4−) show localization of HA-D126A-RHO-4 to septa. (K) Actin localization in CR31-1. Arrow points to a completed septum without any actin staining. (L) DIC image of K. Bar, 10 μm.