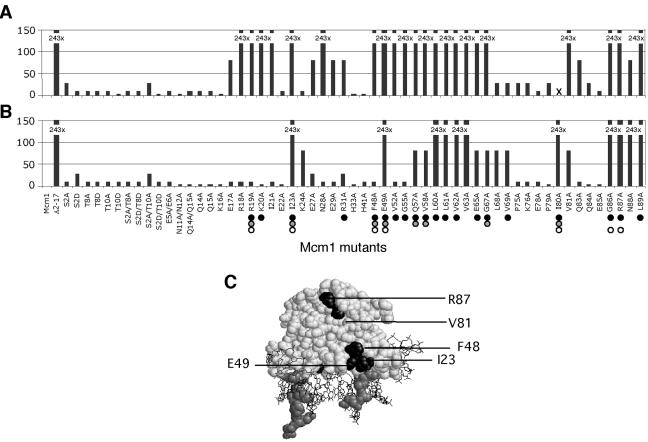
FIG. 4.
Effects of amino acid substitutions in Mcm1 on CFW and alkaline pH tolerance. Each of the indicated mutants was assayed for growth on YEPD medium with 25-mg/ml CFW (A) and alkaline pH 8.5 (B). Bars represent the fold decrease in growth of the Mcm1 mutations indicated at the bottom, relative to wild-type MCM1. X, a mutant that was not tested. Mutants that affect activation in complex with α1 (dark circles), Ste12 (gray circles), or Mcm1 on its own (open circles) are shown for comparison (28). (C) Model of the Mcm1 dimer bound to DNA and positions of mutations (highlighted in black) that result in significant growth defects on CFW and alkaline pH. Residues 15 to 22 that form part of the NT arm are shaded gray. The protein is shown in spacefill and the DNA is shown as a wireframe.