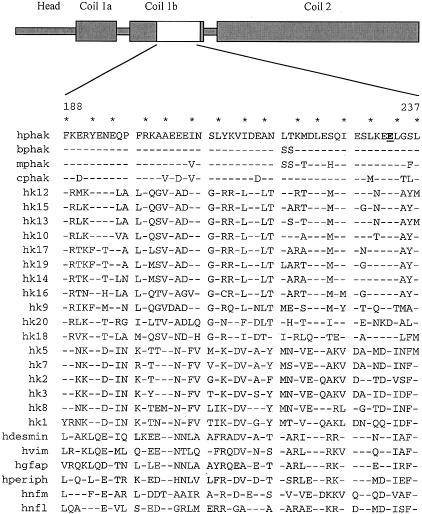
Figure 2.
Domain structure of human phakinin (hphak) (top). “Coil” domains predicted to mediate assembly of coiled-coil dimers are noted. Shown below are the amino-acid sequences of residues 188–237 of hphak and of homologous regions from 26 other IF proteins. Residues 1 and 4 of the alpha helical heptad repeats of hphak are starred. Glutamic acid 233 of hphak is underlined and appears in boldface type. Residues in the other IF proteins identical to those at homologous positions of hphak are indicated by dashes. Abbreviations for other IF proteins are as follows: mphak, murine phakinin; bphak, bovine phakinin; cphak, chicken phakinin; hk1–hk20, human keratins type 1–type 20; hvim, human vimentin (type 3); hdesmin, human desmin (type 3); hperiph, human peripherin; hgfap, human glial fibrillary acidic protein; hnfl, human neurofilament light chain; and hnfm, human neurofilament medium chain.