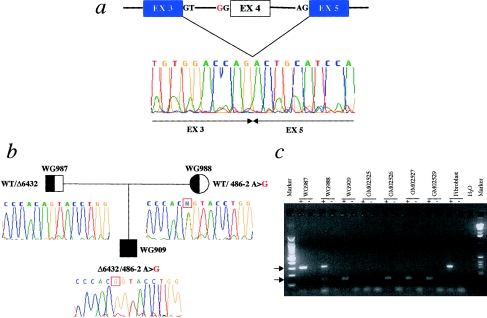
Figure 3.
Mutation 486-2A→G in patients with MLIV. a, Lack of 165 bp, corresponding to exon 4 skipping, observed, at the cDNA level, by RT-PCR. The electropherogram shows the cDNA sequence across the deletion. The mutated allele encodes a truncated protein that retains only the first 21 amino acids of the wild-type allele. The region of homology to the PKD2 gene family is deleted in this mutant. b, 486-2A→G mutation, which segregates with the disease in the family of patient WG909. The electropherograms indicate the genomic sequences surrounding the 486-2A→G mutation. The mother is a carrier of the mutation, showing heterozygosity at the 486-2 position, whereas the father, who is a carrier of the Δ6432 allele, is hemizygous for a portion of the ML4 gene (see fig. 2b and text). The WG909 proband is a compound heterozygote for the 486-2A→G and Δ6432 mutations. c, RT-PCR of RNA from fibroblast cell lines, performed with primers located on exons 3 (MC21E) and 5 (MC21B) (see the Patients, Material, and Methods section). An altered size fragment, of 142 bp (lower arrow), is amplified in patients WG909, GM02526, GM02527, and GM02529 and in the carrier mother, WG988. The wild-type fragment, of 307 bp (upper arrow), is present only in the unaffected parents—WG987 and WG988—and in the fibroblast control cDNA sample. A plus sign (+) and a minus sign (−) denote, respectively, the presence and absence of RT in the RT-PCR. H2O = the negative control. No amplification product is observed in patient GM02525, who is homozygous for the Δ6432 deletion, which removes this portion of the gene. The cDNA of patient GM02533A was not available.