Figure 1.
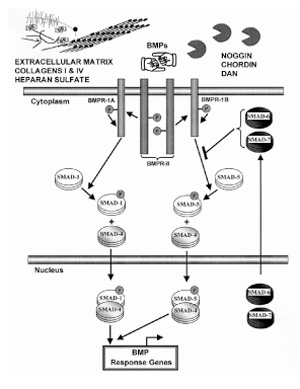
BMP receptors and signaling cascades. BMPs are dimeric ligands with a cysteine knot in each monomer fold. Each monomer has two β sheets (represented as two pointing fingers). These fingers in the functional dimer are oriented in opposite directions. BMPs interact with both type I and type II BMP receptors (BMPR-I and BMPR-II). The exact stoichiometry of the receptor complex is currently being elucidated. BMPR-II phosphorylates the glycine-serine (GS) domain of BMPR-I. The collaboration between type I and type II receptors forms the signal transducing complex. The BMP type I receptor kinase complex phosphorylates the trimeric signaling substrate Smad 1 or Smad 5. This phosphorylation is inhibited and modulated by inhibitory Smad 6 and Smad 7. Phosphorylated Smad 1 or Smad 5 interacts with Smad 4 (functional partner) and enters the nucleus to activate the transcriptional machinery for early BMP response genes. A novel Smad interacting protein may interact and modulate the binding of heteromeric Smad 1/Smad 4 complexes to the DNA. The bioavailability of BMP for interaction with BMP receptors is determined by binding to extracellular matrix components such as heparan sulfate and collagen IV. The BMP antagonists noggin, chordin and DAN can also bind with high affinity to BMP and prevent interaction with receptors. There is thus a very intricate regulation of BMP biological actions.
