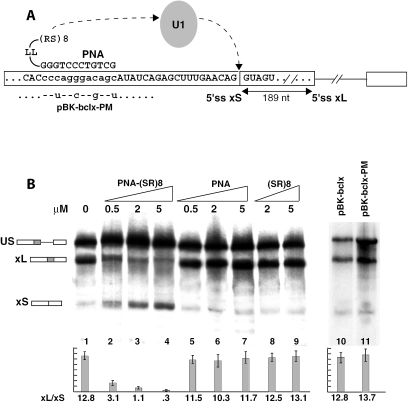
Figure 3.
A PNA oligo conjugated to an SR domain switches splicing to bcl-xS in vitro. (A) Schematic representation of the PNA-SR oligonucleotide, the location of its target sequence on the bcl-x transcript and likely mechanism of activation of the -xS splice site through recruitment of U1 snRNP. The mutations in the pBK-bclx-PM substrate are indicated. (B) In vitro splicing reactions. Increasing amounts of PNA-(SR)8 oligo, the control PNA oligo or the SR peptide alone were added to in vitro splicing reactions containing HeLa nuclear extract and the pBK-bclx substrate. The splicing profiles of pBK-bclx and pBK-bclx-PM are compared (lanes 10–11). Splicing ratios and error bars have been obtained from three independent experiments.